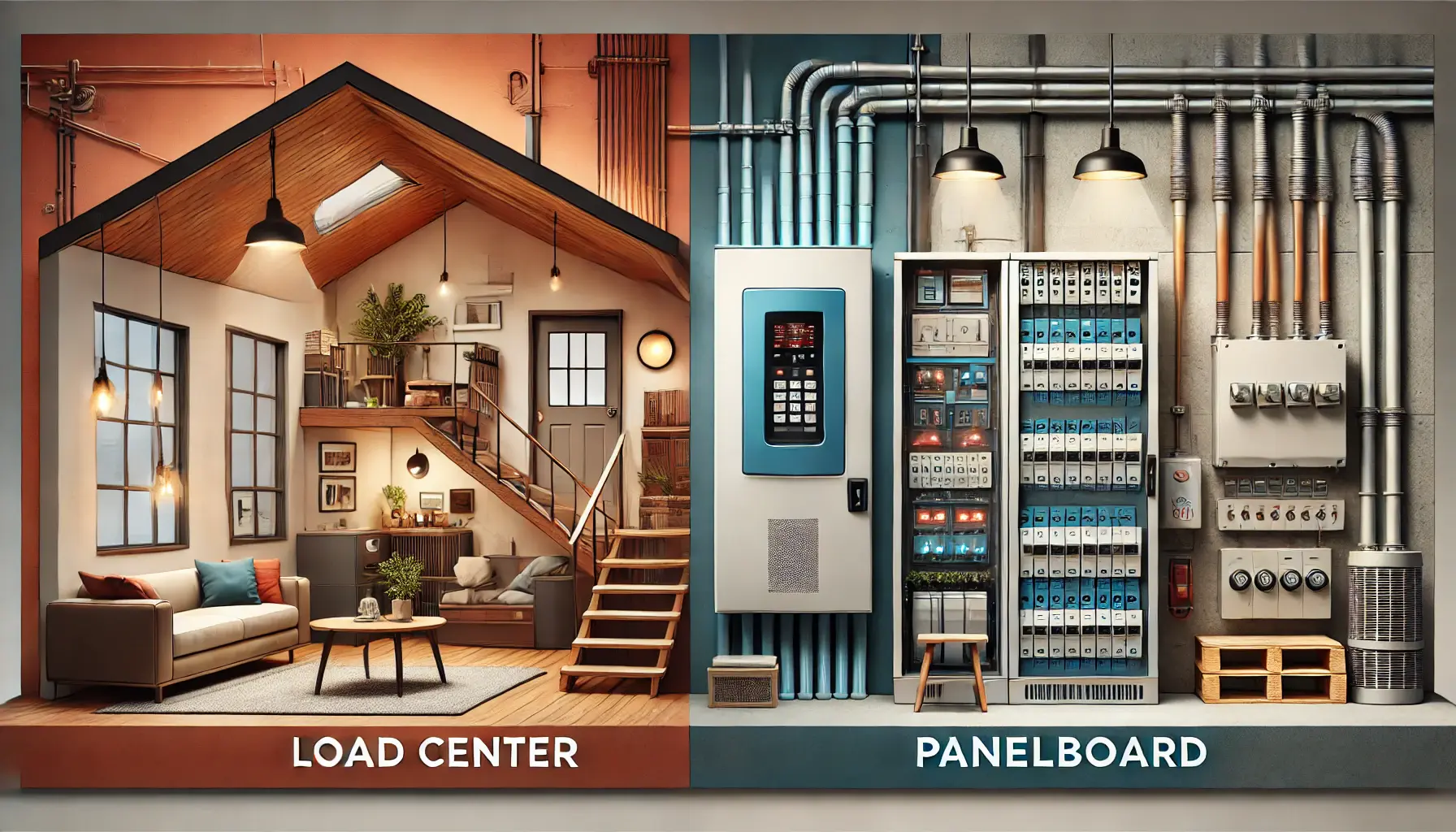
When discussing electrical power distribution, two key components often come up: Load Centers and Panelboards. These devices, while similar in some functions, serve distinct purposes and are designed for different applications. Known by various names, such as Breaker Box, Distribution Board, or Switchboard, they form the backbone of electrical systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
This article provides a detailed comparison of Load Centers and Panelboards, their structures, functions, and how smart monitoring technologies enhance their performance.
Introduction to Load Centers and Panelboards
Load Centers
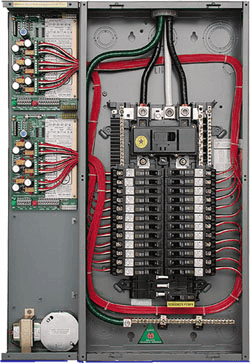
A Load Center, commonly referred to as a Breaker Box or Residential Electrical Panel, is primarily used in residential and small commercial applications to distribute power and protect circuits.
Features:
- Typically installed indoors, such as in garages, basements, or closets.
- Designed for 120/240V single-phase power systems.
- Equipped with plug-on breakers for easy installation and maintenance.
- Maximum current capacity: Usually up to 400 amps.
Panelboards
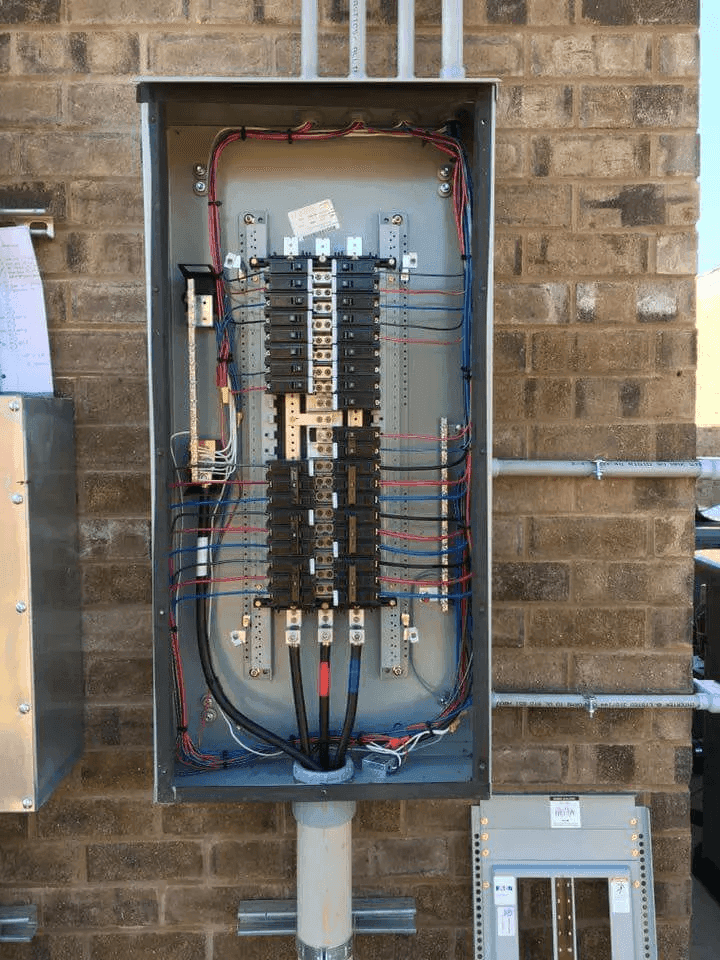
A Panelboard, also known as a Distribution Board or Electrical Control Panel, is used in commercial and industrial settings where higher voltage and greater capacity are required.
Features:
- Handles both single-phase and three-phase power systems (120/240V or 208/480V).
- Equipped with bolt-on breakers, providing a more secure connection for high-load applications.
- Maximum current capacity: Can exceed 1,200 amps.
Detailed Structural Differences
Core Components
| Component | Load Center | Panelboard |
|---|---|---|
| Main Breaker | Controls the entire power supply to the home. | Handles higher capacity with robust breakers. |
| Branch Circuit Breakers | Protects individual circuits (plug-on type). | Supports both plug-on and bolt-on types. |
| Neutral and Ground Bars | Connect to neutral and ground wires to prevent overcurrent. | Similar but with higher capacity and more grounding options. |
| Bus Bars | Thin copper or aluminum strips for circuit distribution. | Larger bus bars to handle higher loads. |
Internal Layout Example
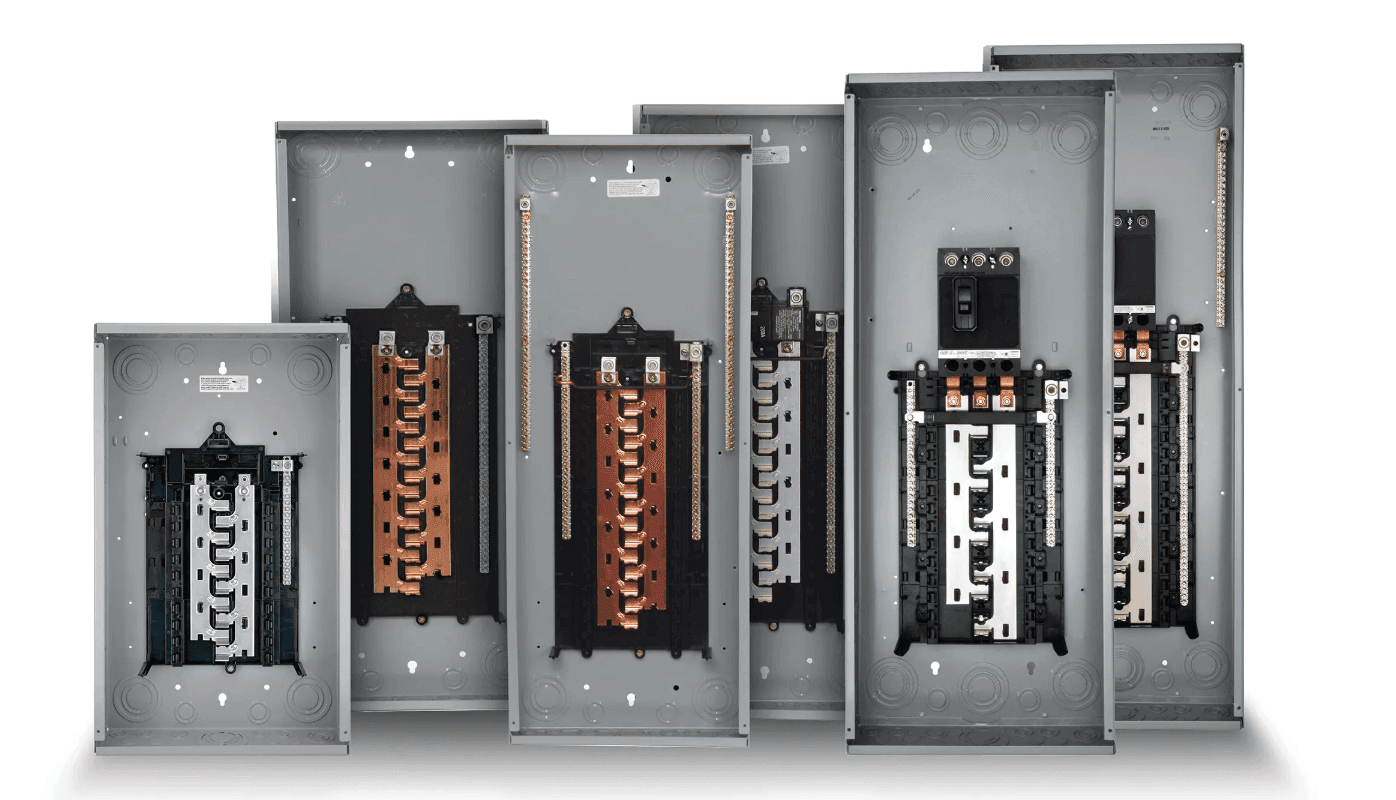
Key Differences Between Load Centers and Panelboards
Design and Construction
| Aspect | Load Center | Panelboard |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Smaller, compact for residential use. | Larger, modular design for commercial and industrial use. |
| Mounting | Flush or surface-mounted on walls. | Wall-mounted or standalone in dedicated rooms. |
| Material | Lightweight metal or plastic casing. | Heavy-duty steel or aluminum casing for durability. |
Electrical Capacity
| Aspect | Load Center | Panelboard |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 120/240V single-phase. | 120/240V single-phase or 208/480V three-phase. |
| Current Capacity | Up to 400 amps. | Can exceed 1,200 amps. |
Applications
| Aspect | Load Center | Panelboard |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Residential buildings, light commercial. | Commercial, industrial, and high-load environments. |
| Example Scenarios | Powering lights, appliances, and HVAC. | Managing power for industrial equipment and large offices. |
Smart Monitoring Capabilities
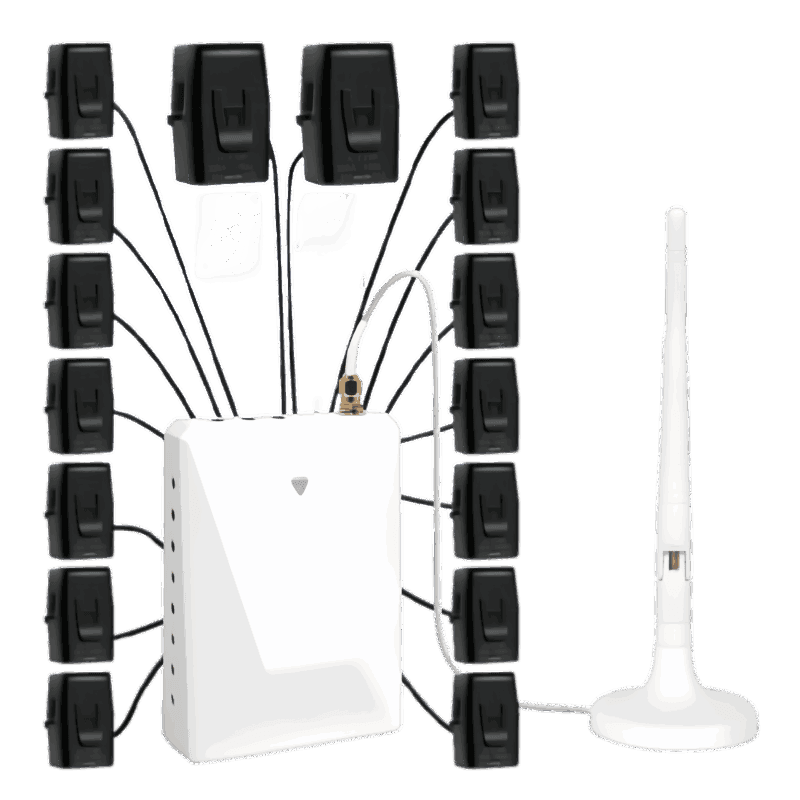
With advancements in technology, Load Centers and Panelboards can now be integrated with Energy smart monitoring systems. These systems provide real-time data on power usage, circuit status, and potential issues. And mainly there should be Smart Electric Monitor integrated.
Benefits of Smart Monitoring
- Energy Efficiency: Track energy consumption to identify inefficiencies and reduce costs.
- Preventive Maintenance: Monitor circuit performance and detect potential overloads or faults before they cause damage.
- Remote Control: Use apps or connected devices to control circuits and manage energy use remotely.
- Data Analysis: Generate reports to optimize power distribution and plan for upgrades.
How It Works
- Sensors: Installed on bus bars or breakers to measure voltage, current, and power consumption.
- Connectivity: Data is transmitted to a central hub via Wi-Fi, Zigbee, or other IoT protocols.
- User Interface: Accessible through mobile apps or desktop dashboards for real-time insights.
Example Smart Monitoring Solutions
| Brand & Model | Photos | Feature | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grus WattPanel-2X |  | Provides real-time energy usage tracking and remote Split-phase breaker control. Monitoring 240V Main Load Center and 0 ~ 16 individual circuits . | Residential and small business Load Centers |
| Grus WattPanel-3X |  | Advanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance for panelboards. Industrial Energy Advanced Three-Phase Multi-Circuit Monitoring. 208V ~ 400V main load Usage and and 0 ~ 16 individual circuits . | Commercial and industrial environments Panelboard. |
| Grus WattNet-3 |  | Supports multi-panel integration and energy optimization. Three-Phase Smart Electric Meter. Clamp-On CT for Bi-Directional Power Monitoring. No individual circuits. | Smaller commercial spaces or light industrial Panelboard. |
| Grus WattNet-1 |  | Single Phase Electric Meter. Supports at most 2 circuits. Monitor Bi-Directional Power Meter. | Residential and small business circuits. |
Real-World Examples and Applications
Residential Example: Load Center
Imagine a standard suburban home with a Load Center installed in the garage. This Load Center distributes power to the home's lighting circuits, kitchen appliances, HVAC system, and outdoor outlets.
Key Features in Use:
- Plug-On Breakers: Homeowners can easily add or replace circuits for new appliances, such as an EV charger or a hot tub.
- 120/240V Distribution: Circuits deliver 120V for standard outlets and lighting, while 240V supports the HVAC system and larger appliances like an electric oven.
- Smart Monitoring: A Wi-Fi-enabled Load Center allows the homeowner to track energy usage via a smartphone app, enabling better control over energy bills.
Challenges Addressed:
- Avoiding overloaded circuits by monitoring real-time usage.
- Scheduling appliances to run during off-peak energy rates.
- Detecting and addressing circuit faults remotely.
Commercial Example: Panelboard
Consider a small manufacturing facility using a Panelboard to distribute power to various production lines, lighting systems, and administrative offices.
Key Features in Use:
- Bolt-On Breakers: Ensure secure connections for high-vibration environments like motorized equipment.
- Three-Phase Power: Supports high-efficiency power distribution to heavy machinery.
- Modular Design: Allows for future expansion by adding new circuits as production lines grow.
Challenges Addressed:
- Balancing power loads across multiple machines to prevent downtime.
- Using smart monitoring to predict and prevent equipment failures.
- Supporting energy audits for compliance and cost-saving initiatives.
Advanced Smart Features for Load Centers and Panelboards
As power systems become more sophisticated, manufacturers are integrating advanced smart technologies into Load Centers and Panelboards. Below are some key innovations.
1. Circuit-Level Monitoring
Smart Load Centers and Panelboards allow users to track power consumption at the circuit level. This feature provides:
- Detailed energy usage reports.
- Identification of energy-hungry devices.
- Insights for optimizing load distribution.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Using AI and machine learning, smart systems can:
- Detect patterns in power usage that indicate potential equipment failures.
- Send alerts for preventive maintenance before issues escalate.
- Reduce downtime by scheduling maintenance proactively.
3. Renewable Energy Integration
Modern systems can integrate with renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines, allowing users to:
- Monitor energy production and consumption in real-time.
- Prioritize the use of renewable energy to reduce reliance on the grid.
- Store excess energy in battery systems for later use.
Choosing Between Load Centers and Panelboards
Key Factors to Consider
| Factor | Load Center | Panelboard |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Requirements | For 120/240V single-phase systems. | For 120/240V single-phase or 208/480V three-phase systems. |
| Load Capacity | Up to 400 amps. | Can exceed 1,200 amps. |
| Installation Location | Residential or light commercial settings. | Commercial, industrial, or high-load environments. |
| Smart Features | Basic energy tracking and remote control. | Advanced diagnostics, energy optimization, and predictive maintenance. |
Example Scenarios
- For a Homeowner
- A Load Center is the best choice for managing standard home circuits, especially with smart monitoring features that allow energy tracking and remote breaker control.
- For a Small Business
- A Panelboard offers greater flexibility for powering office equipment, lighting, and HVAC systems, with the ability to expand as the business grows.
- For an Industrial Facility
- A high-capacity Panelboard with smart monitoring ensures reliability for critical equipment and reduces downtime with predictive maintenance.
Conclusion
Load Centers and Panelboards are both integral to modern electrical systems, but they serve different needs based on capacity, functionality, and application. Load Centers excel in residential settings, offering simplicity, affordability, and the ability to handle basic power distribution. Panelboards, on the other hand, are designed for commercial and industrial use, providing higher capacity, modularity, and robust features.
The integration of smart monitoring technology has further enhanced both devices, making them more efficient, reliable, and user-friendly. Whether you're managing a home, a business, or an industrial facility, understanding these differences ensures you choose the right solution for your power distribution needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can a Load Center be used in a commercial setting?
Yes, but only in light commercial applications with moderate power requirements. For larger systems, a Panelboard is recommended.
2. How does smart monitoring improve energy efficiency?
Smart monitoring provides real-time data on energy usage, allowing users to optimize load distribution, identify inefficiencies, and reduce costs.
3. Are Load Centers and Panelboards interchangeable?
No. While they share some similarities, Load Centers are tailored for residential use, while Panelboards are designed for higher-capacity commercial and industrial applications.
4. What brands offer smart Load Centers and Panelboards?
- Load Centers: Schneider Electric, Siemens, Eaton.
- Panelboards: Eaton Power Xpert, Square D by Schneider Electric.
By understanding the unique roles and capabilities of Load Centers and Panelboards, you can make informed decisions for your electrical system, whether for a home, business, or industrial application.