Alternating Current (AC) power supply is the standard method for delivering electricity to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. The voltage levels and phase configurations differ depending on the application. In this article, we will:
✅ Explain the waveform characteristics of 120V single-phase, 120V/240V split-phase, and 120V/208V three-phase systems
✅ Illustrate the sinusoidal voltage waveforms for each system
✅ Demonstrate how voltage calculations are performed for different configurations
1. 120V Single-Phase AC Waveform
🔹 Commonly used for:
✔ Standard household outlets
✔ Lighting circuits
✔ Small appliances
Characteristics:
- RMS Voltage: 120V
- Peak Voltage Calculation:
$$V_{\text{peak}} = V_{\text{RMS}} \times \sqrt{2} = 120V \times 1.414 = 170V$$ - Frequency: 60Hz (one complete cycle every 16.67ms)
- Voltage oscillates between +170V and -170V
The following figure illustrates the 120V AC sine wave:
2. 120V/240V Split-Phase AC Waveform
🔹 Commonly used for:
✔ Residential electrical systems
✔ High-power appliances (electric ovens, HVAC, water heaters, EV chargers)
How it works:
- A center-tapped transformer provides two hot wires (L1 and L2) and one neutral (N).
- L1 to Neutral (120V), L2 to Neutral (120V), and L1 to L2 (240V).
- L1 and L2 are 180° out of phase, meaning their waveforms are exact opposites.
Voltage Calculation for 240V:
$$V_{\text{peak}} = 240V \times \sqrt{2} = 339V$$
The figure below illustrates the 120V/240V split-phase sine wave:
3. 120V/208V Three-Phase Wye AC Waveform
🔹 Commonly used for:
✔ Commercial buildings
✔ Multi-unit residential buildings
✔ Data centers & IT infrastructure
How it works:
- A three-phase wye transformer provides L1, L2, L3, and Neutral (N).
- Each phase to neutral (L1-N, L2-N, L3-N) is 120V.
- Each phase pair (L1-L2, L2-L3, L1-L3) is 208V due to the 120° phase shift.
Voltage Calculation for 208V:
$$V_{\text{L1-L2}} = V_{\text{L1-N}} + V_{\text{L2-N}} = 120V + 120V = 240V$$
$$V_{\text{Line}} = V_{\text{Phase}} \times \sqrt{3} = 120V \times 1.732 = 208V$$
The figure below illustrates the 120V/208V three-phase wye sine waves:
4. Visualizing the Voltage Waveforms
Below are the plotted waveforms for 120V single-phase, 120V/240V split-phase, and 120V/208V three-phase AC systems.
📌 Key Observations from the Graphs:
- 120V Single-Phase: One sine wave oscillating between +170V and -170V.
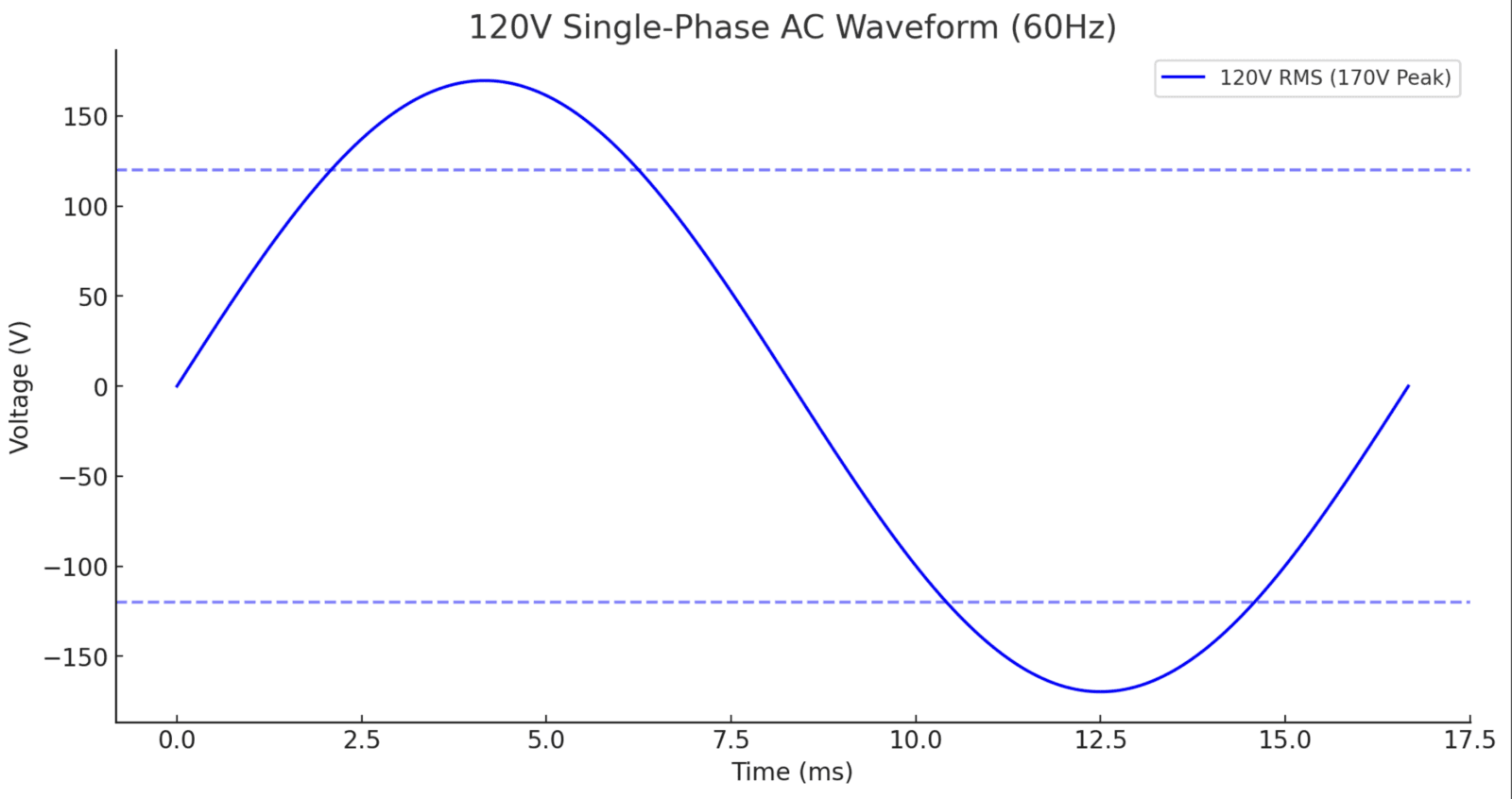
- Standard home socket, 60Hz, sine wave, Peak voltage 170V.
- The AC cycle is 16.67ms (1/60Hz).
- 120V/240V Split-Phase: L1 and L2 are 180° out of phase, producing 240V across L1-L2.
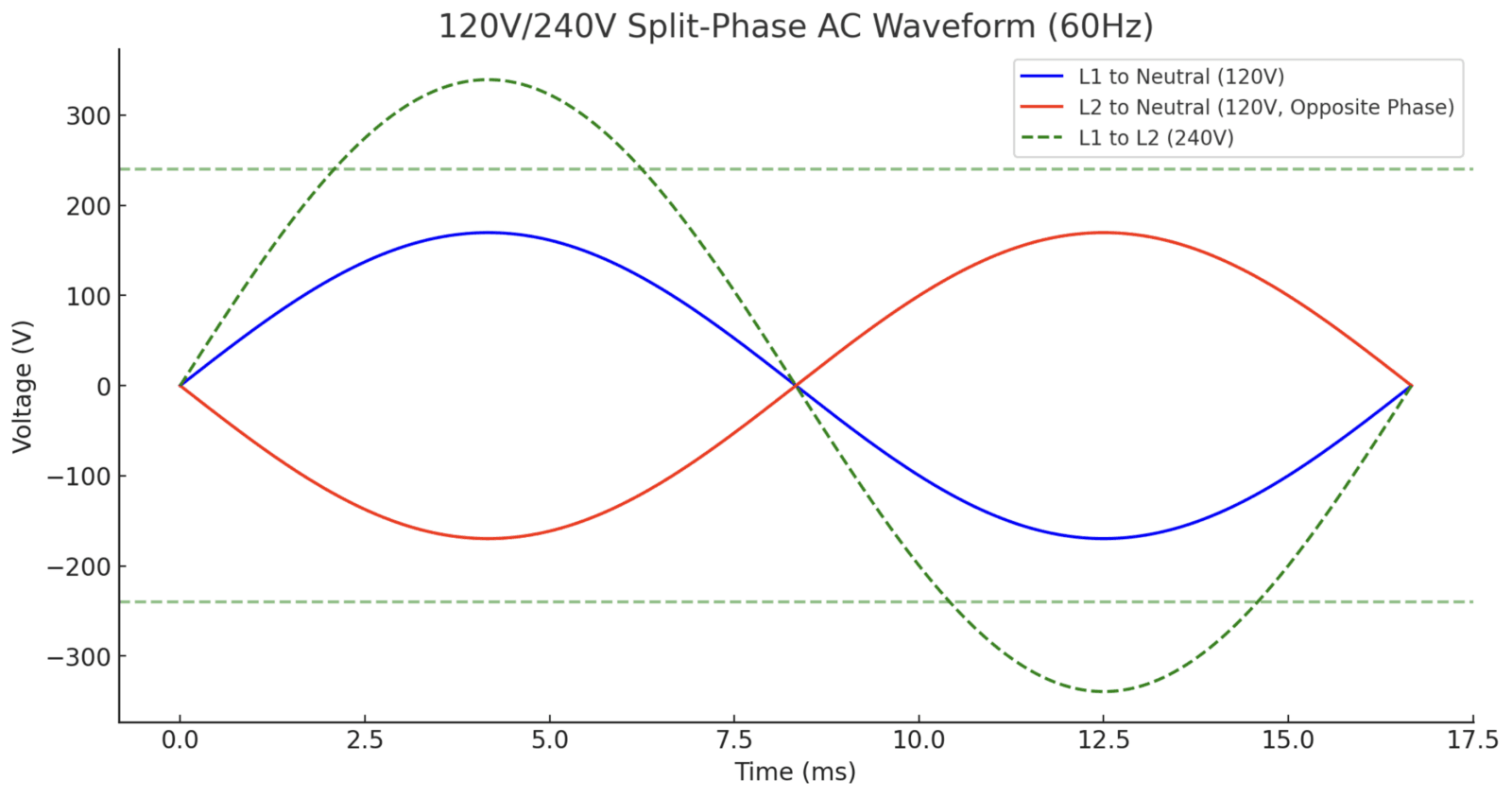
- L1 and L2 differ by 180°, resulting in a 240V differential voltage.
- L1→N and L2→N are both 120V, L1→L2 forms the 240V power supply for high power devices (such as EV chargers, air conditioners).
- 120V/208V Three-Phase Wye: L1, L2, and L3 are 120° apart, forming 208V between any two phases.
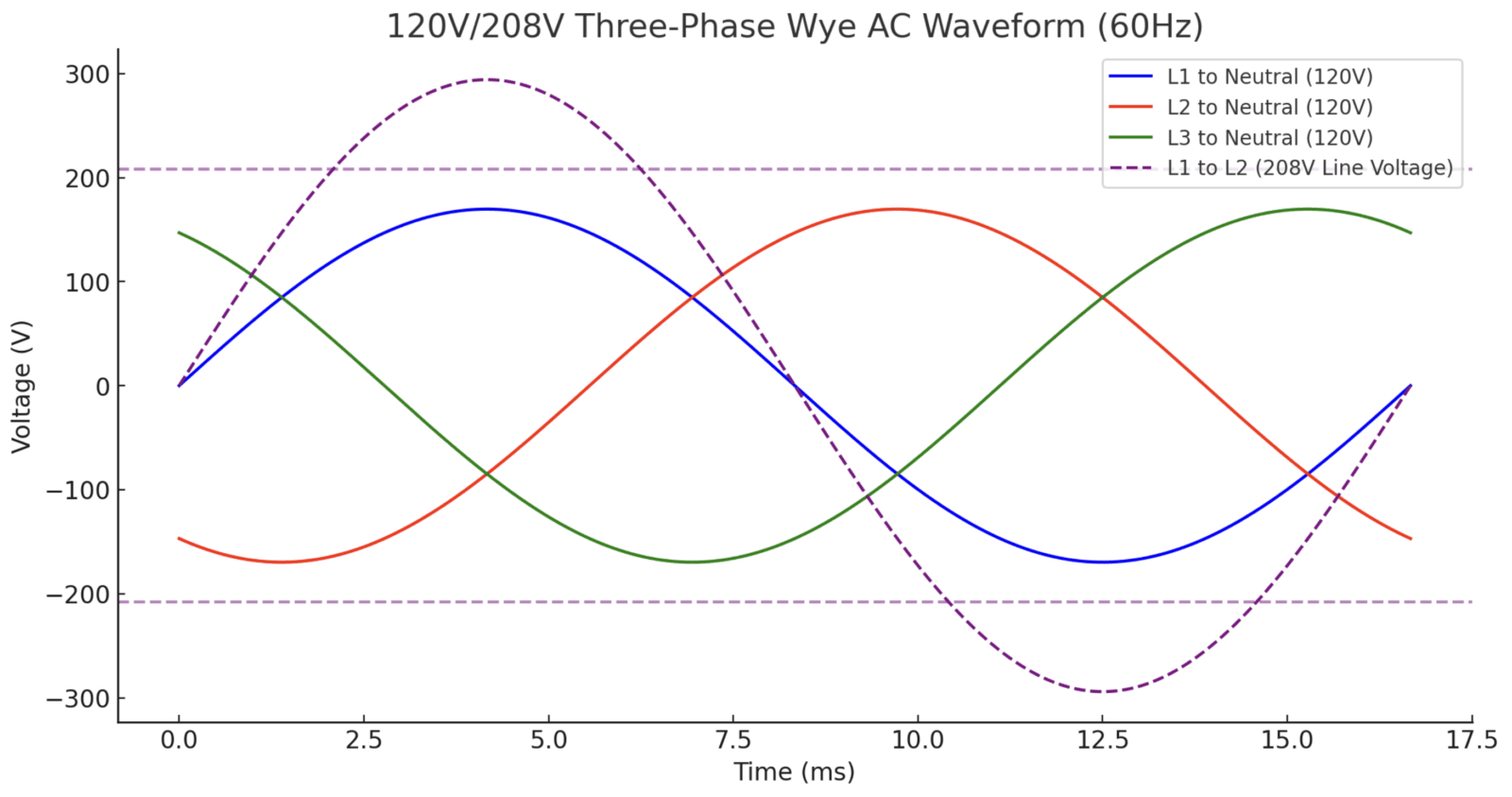
- L1, L2, L3 differ by 120°.
- L1, L2, L3 → Neutral = 120V for single-phase loads (lighting, office equipment).
- L1 → L2, L2 → L3, L1 → L3 = 208V for three-phase loads (motors, commercial HVAC).
5. Why Understanding Voltage Waveforms Matters?
Understanding AC voltage waveforms is crucial for designing electrical systems, balancing loads, and improving energy efficiency.
💡 Practical Applications:
✔ Homeowners & electricians – Choosing the right voltage for appliances
✔ Business owners – Optimizing energy efficiency in commercial spaces
✔ Data centers & factories – Ensuring balanced three-phase power distribution
🔹 Choosing the Right Smart Energy Monitor:
| Smart Meter | Best For | Compatible Voltage System |
|---|---|---|
| WattNet-3 | General three-phase energy monitoring | 120/208V, 277/480V Three-Phase (Wye) |
| WattPanel-3X | Advanced multi-channel load monitoring | 120/208V, 277/480V Three-Phase |
📌 Monitoring voltage and current waveforms with smart meters ensures optimal energy distribution and cost savings.
6. Conclusion: Optimizing Energy Usage Based on Voltage Systems
Understanding 120V, 120V/240V, and 120V/208V waveforms allows better load balancing, energy efficiency, and electrical system design.
✅ Key Takeaways:
- 120V Single-Phase: Standard for home outlets and small appliances.
- 120V/240V Split-Phase: Used in residential homes for high-power loads.
- 120V/208V Three-Phase: Common in commercial buildings, balancing power efficiently.
🚀 **Upgrade your energy monitoring with Grus Smart Meters today!