Most homeowners don’t think about how electricity enters their homes, but the type of power phase used can impact appliance efficiency, energy costs, and electrical compatibility. In the U.S., residential properties primarily use split-phase power (120/240V), but why?
This guide will explain:
✅ What phase is normal American home power?
✅ The differences between Single-Phase, Split-Phase, and Three-Phase power
✅ Where each type is used and why it matters
✅ How smart meters like Grus Smart Meters can help you monitor home energy consumption
Whether you’re looking to install a new appliance, monitor energy usage, or understand how your home is wired, this guide will break down everything you need to know.
1. What Phase is Normal American Home Power?
1.1 Most U.S. Homes Use Split-Phase 120/240V Power
In the U.S., the standard home electrical supply is split-phase (120/240V). This system provides:
✔ 120V power for small appliances and lighting.
✔ 240V power for high-energy appliances like dryers, ovens, and EV chargers.
🔹 Why Split-Phase Power?
- Balanced Power Distribution – Prevents overloading circuits.
- Supports Both Small & Large Appliances – From LED bulbs to EV chargers.
- More Efficient Than Single-Phase – Allows for higher power loads when needed.
1.2 How Split-Phase Power Works
A split-phase system has three main conductors:
✔ L1 (Hot Line 1)
✔ L2 (Hot Line 2)
✔ Neutral Wire
The voltage breakdown:
| Connection Type | Voltage Output | Used For |
|---|---|---|
| L1 to Neutral | 120V | Standard outlets, lights, small appliances |
| L2 to Neutral | 120V | Additional household circuits |
| L1 to L2 | 240V | High-power devices (stoves, dryers, EV chargers) |
graph TD; A["Power Grid (Split-Phase)"] -->|"L1 (120V to Neutral)"| B["Home Main Panel"] A -->|"L2 (120V to Neutral)"| B B -->|"L1 to Neutral (120V)"| C["Standard Outlets & Appliances"] B -->|"L2 to Neutral (120V)"| D["More Household Circuits"] B -->|"L1 to L2 (240V)"| E["High-Power Devices (Dryer, Oven, EV Charger)"]
💡 Example:
- Your lights, TV, and refrigerator run on 120V circuits.
- Your electric stove, dryer, and EV charger require 240V from the L1-to-L2 connection.
🔹 Key Takeaway: Most American homes use split-phase power (120/240V) because it supports both small and high-power loads efficiently.
2. Single-Phase Power: What Is It & Where Is It Used?
2.1 What Is Single-Phase Power?
Single-phase power consists of one hot wire (L1) and one neutral wire. It is commonly used in:
✔ Small apartments
✔ Rural homes with low power demand
✔ Basic residential lighting and small appliances
2.2 How Single-Phase Power Works
A single-phase system delivers power in one alternating current (AC) cycle, which can cause voltage fluctuations. It is less efficient for high-power loads compared to split-phase.
| Connection Type | Voltage Output | Used For |
|---|---|---|
| L1 to Neutral | 120V | Lights, TVs, small appliances |
graph TD; A["Power Grid (Single-Phase)"] -->|"L1 (120V to Neutral)"| B["Home Main Panel"] B -->|"L1 to Neutral (120V)"| C["Lights, Fans, Small Appliances"]
🔹 Key Takeaway: Single-phase power is used in small residential settings but lacks the flexibility of split-phase power.
3. Three-Phase Power: What Is It & Where Is It Used?
3.1 What Is Three-Phase Power?
Unlike single-phase (L1, Neutral) and split-phase (L1, L2, Neutral) power, a three-phase electrical system consists of:
✔ Three Hot (Live) Wires (L1, L2, L3)
✔ One Neutral Wire (optional, depending on the system configuration)
Three-phase power is primarily used for:
✅ Industrial plants
✅ Large commercial buildings
✅ Manufacturing facilities
✅ Data centers
Advantages of Three-Phase Power
✔ Continuous power flow – Prevents voltage dips by ensuring constant electrical delivery.
✔ Handles high loads efficiently – Used for heavy-duty machinery, industrial HVAC systems, and large motors.
✔ Balanced power distribution – Prevents overloading any single phase.
3.2 How Three-Phase Power Works
A three-phase system supplies three alternating currents, each 120 degrees out of phase, ensuring that at least one conductor is always delivering power. This makes it ideal for:
| Connection Type | Voltage Output | Used For |
|---|---|---|
| L1 to Neutral | 120V | Office lighting, small circuits |
| L2 to Neutral | 120V | More lighting circuits |
| L3 to Neutral | 120V | Office computers, small appliances |
| L1 to L2 | 208V | Commercial-grade HVAC systems |
| L2 to L3 | 208V | Manufacturing equipment |
| L1 to L3 | 208V | Heavy industrial loads |
graph TD; A["Power Grid (Three-Phase)"] -->|"L1 120V to Neutral"| B["Commercial Main Panel"] A -->|L2 120V to Neutral| B A -->|L3 120V to Neutral| B B -->|L1 to L2 208V| C["Heavy Machinery"] B -->|L2 to L3 208V| D["Industrial HVAC"] B -->|L1 to L3 208V| E["Manufacturing Equipment"]
🔹 Key Takeaway: Three-phase power is used in commercial and industrial applications due to its ability to handle large loads efficiently.
4. How to Identify Your Home’s Power Phase
4.1 Check Your Main Electrical Panel
You can determine your power phase by inspecting your home’s electrical panel:
✔ Single-Phase Power: One main breaker with two wires (hot & neutral) → Single-phase 120V
✔ Split-Phase Power: Two main breakers with three wires (L1, L2, and Neutral) → Split-phase 120/240V
✔ Three-Phase Power: Three main breakers with four wires (L1, L2, L3, and Neutral) → Three-phase 120/208V or 277/480V
4.2 Check Your Utility Meter
Some utility meters display voltage ratings:
- If it shows 120V only, your home has single-phase power.
- If it lists 120/240V, your home has split-phase power.
- If it lists 208V or 480V, your building uses three-phase power.
4.3 Ask Your Power Utility or Electrician
If you are unsure about your home's power phase, contact your utility company or consult a licensed electrician.
5. Best Smart Energy Meters for Different Power Phases
Now that you understand the differences between Single-Phase, Split-Phase, and Three-Phase power, the next step is choosing the right smart energy meter for monitoring and optimizing home energy usage.
5.1 Why Use a Smart Energy Meter?
A smart energy meter helps homeowners and businesses:
✔ Track real-time energy usage to identify high-power devices.
✔ Optimize power distribution to reduce electricity costs.
✔ Detect unusual energy spikes that could indicate faulty appliances.
✔ Monitor solar, battery, and grid energy flow for energy efficiency.
5.2 Choosing the Right Smart Meter Based on Power Phase
| Power Phase | Voltage Type | Best Smart Meter | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Phase (L1, Neutral) | 120V | Single-Phase Smart Meter | Small homes, apartments |
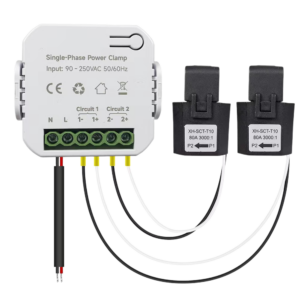
| Split-Phase (L1, L2, Neutral) | 120/240V | Grus Split-Phase Electric Monitor | Most American homes |
| Three-Phase (L1, L2, L3, Neutral) | 120/208V or 277/480V | Three-Phase Smart Meter Multi-Circuit Energy Monitor | Industrial & commercial use |
💡 Best Residential Solution: The Grus Split-Phase Electric Monitor is ideal for homeowners with split-phase power looking to monitor and optimize their electricity usage.
6. How to Monitor Home Energy Usage in Real-Time
A smart energy meter should be installed at key locations to provide comprehensive energy tracking.
6.1 Where to Install Smart Meters for Home Energy Monitoring
| Smart Meter Location | Purpose | Monitors |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection (Main Panel) | Track total home power usage | Grid import/export |
| Solar Inverter Output | Monitor solar generation | Solar production |
| Battery Storage Input/Output | Track stored and discharged energy | Battery charge/discharge cycles |
| EV Charging Station | Identify charging costs | EV power consumption |
| Home Appliance Panel | Detect high-energy devices | Individual appliance loads |
6.2 How Smart Meters Improve Energy Efficiency
Using AI-powered energy monitoring, a smart meter can:
✅ Predict peak usage times and suggest cost-saving adjustments.
✅ Identify inefficient appliances and provide recommendations.
✅ Help homeowners shift energy usage to off-peak hours to save money.
graph TD; A["Smart Energy Meter"] -->|Real-Time Data Collection| B["AI Energy Analysis"] B -->|Detects Power Waste| C["User Alerts & Suggestions"] C -->|Recommends Off-Peak Usage| D["Energy Cost Optimization"]
🔹 Key Insight: By continuously analyzing power usage, a smart meter helps reduce electricity bills and improve efficiency.
7. Why Grus Smart Meters Are the Best Solution for Home Power Monitoring
If you're looking for a smart way to manage home energy, Grus Smart Meters provide:
✔ Real-Time Energy Tracking – Monitor power usage for grid, solar, and battery systems.
✔ AI-Based Efficiency Optimization – Receive smart suggestions to reduce electricity costs.
✔ Appliance-Level Monitoring – Identify high-energy-consuming devices.
✔ Easy Installation – Works with split-phase (120/240V) and single-phase systems.
✔ Smart Home Integration – Compatible with SmartThings, Home Assistant, and Alexa.
graph TD; A["Grus Smart Meter"] -->|Tracks Grid & Solar Usage| B["Real-Time Energy Dashboard"] A -->|Optimizes Battery Storage| C["Smart Home System"] A -->|Monitors Home Appliances| D["User Reports & Alerts"]
🚀 Why Choose Grus?
- Reduce electricity bills by up to 25%.
- Provides deeper energy insights than standard utility meters.
- Seamlessly integrates with existing smart home systems.
👉 Upgrade to Grus Smart Meters for Smarter Home Energy Management
Key Takeaways:
✅ Most U.S. homes use Split-Phase power (120/240V), providing efficiency and versatility.
✅ Single-Phase power is common in small residences but lacks high-power capacity.
✅ Three-Phase power is used in industrial applications requiring continuous high loads.
✅ Smart energy meters like Grus Smart Meters help track and optimize power usage across all phase types.🚀 Don’t let high energy bills surprise you!
👉 **[Monitor & Optimize Your Home Energy with Grus Smart Meters Today