Thinking About Installing a New Appliance?
Maybe you’re moving into a new home and wondering if your laundry room has the right outlet for a dryer.
Or you’ve just bought a window A/C, a heat pump, or are planning for an EV charger.
One of the first—and most important—questions that comes up is surprisingly simple:
How do I tell if this outlet is 120 volts or 240 volts?
In U.S. homes, both outlet types exist.
Most everyday outlets are 120V, while high-demand appliances often require 240V.
Plugging into the wrong voltage isn’t just inconvenient.
It can cause poor performance, trip breakers, or permanently damage equipment.
The good news is: you don’t need to be an electrician to make an initial check.
This guide will help you understand the difference, recognize common outlet types, and know when it’s time to double-check before installing anything.
Understanding the Basics: 120V vs. 240V in U.S. Homes
Before checking outlet shapes or labels, it helps to understand why both voltages exist.
Most U.S. homes use a split-phase 120/240V electrical system.
That means your house receives two “hot” wires and one neutral from the utility.
Depending on how a circuit is wired, it can deliver either 120 volts or 240 volts.
120V Circuits
- Use one hot wire and one neutral
- Supply standard wall outlets
- Power everyday devices and small appliances
240V Circuits
- Use both hot wires together
- Deliver higher power
- Serve heavy-duty equipment
Quick reference:
| Voltage | Typical Appliances |
|---|---|
| 120 V | Lamps, TVs, laptops, microwaves, coffee makers |
| 240 V | Electric dryers, ovens, water heaters, central A/C, EV chargers |
One common point of confusion is the difference between 110V and 120V outlets. In practice, they’re the same thing. People often use the terms interchangeably, but modern household wiring in the U.S. is standardized at 120V. When you see an appliance label that says “110V,” it’s simply designed to work with today’s 120V supply.
So, think of it this way:
- 120V = everyday living
- 240V = heavy power
Understanding this split is the foundation for recognizing which outlets you’re dealing with in your own home.
Quick Ways to Tell If an Outlet Is 120 V or 240 V
Now let’s move on to the practical side—what does a 240V outlet look like and how it differs from a regular 120V. You don’t need special tools for this first check; just use your eyes and a little common sense.
1. Look at the Outlet Shape
- 120V outlet: The most common style has two vertical slots and one round hole for the ground. You’ll see these everywhere—bedrooms, living rooms, kitchens—for small appliances.
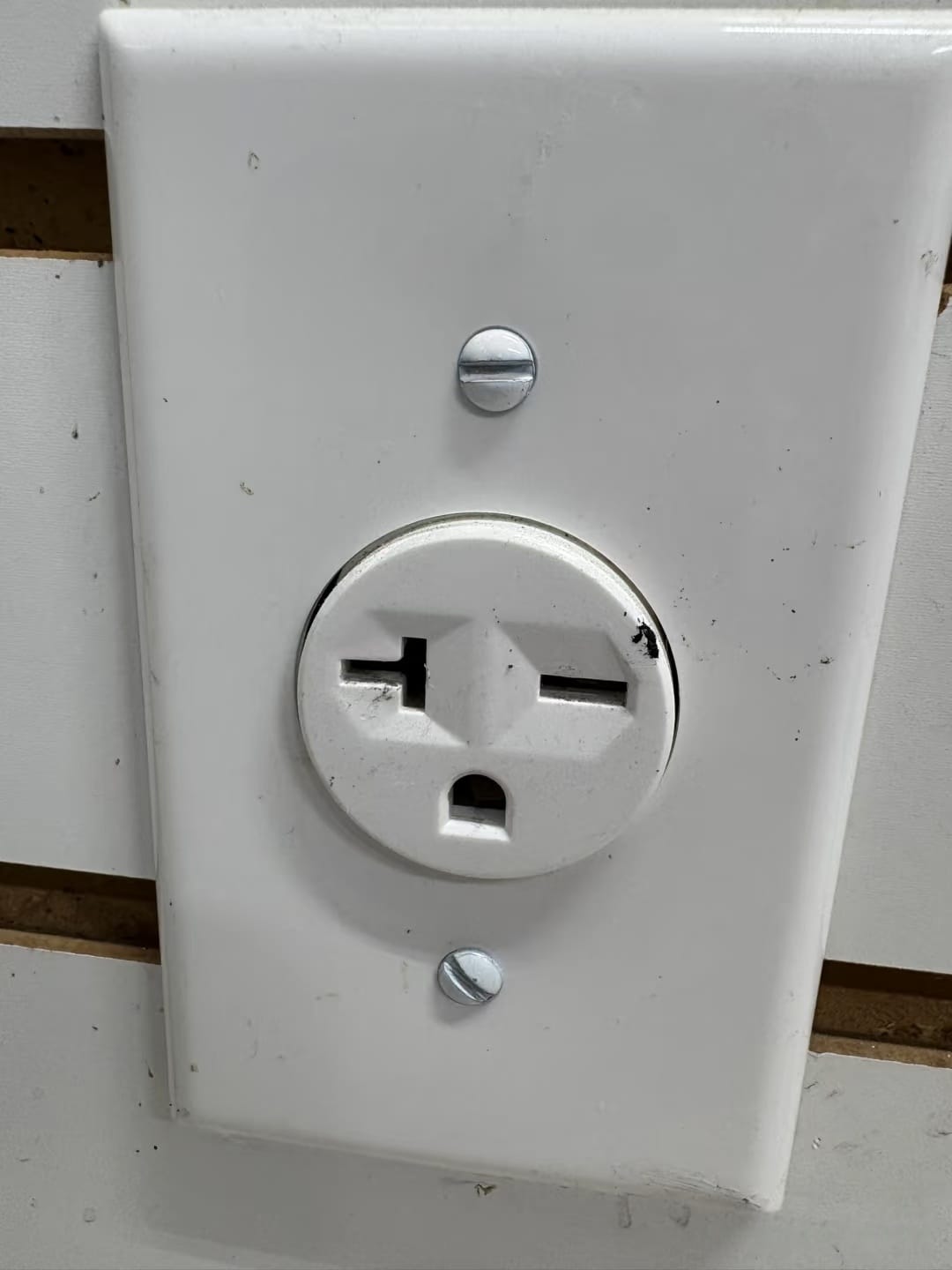
- 240V outlet: Much bulkier. Depending on the appliance, you might see T-shaped slots, L-shaped patterns, or three/four-prong arrangements. These outlets are often larger and may be installed closer to the floor or in utility areas like laundry rooms.
- If you’re still unsure, search for pictures of “120V vs 240V outlet” to compare—visuals make the difference obvious.

2. Check the Plug
Another way to tell is by looking at the appliance plug itself:
- Everyday devices like lamps, toasters, or TVs have slim, two-prong or three-prong plugs that fit into 120V outlets.
- Heavy-duty appliances—dryers, ranges, or EV chargers—come with larger, thicker plugs. These are intentionally designed so they cannot fit into a 120V outlet. This prevents dangerous mismatches.
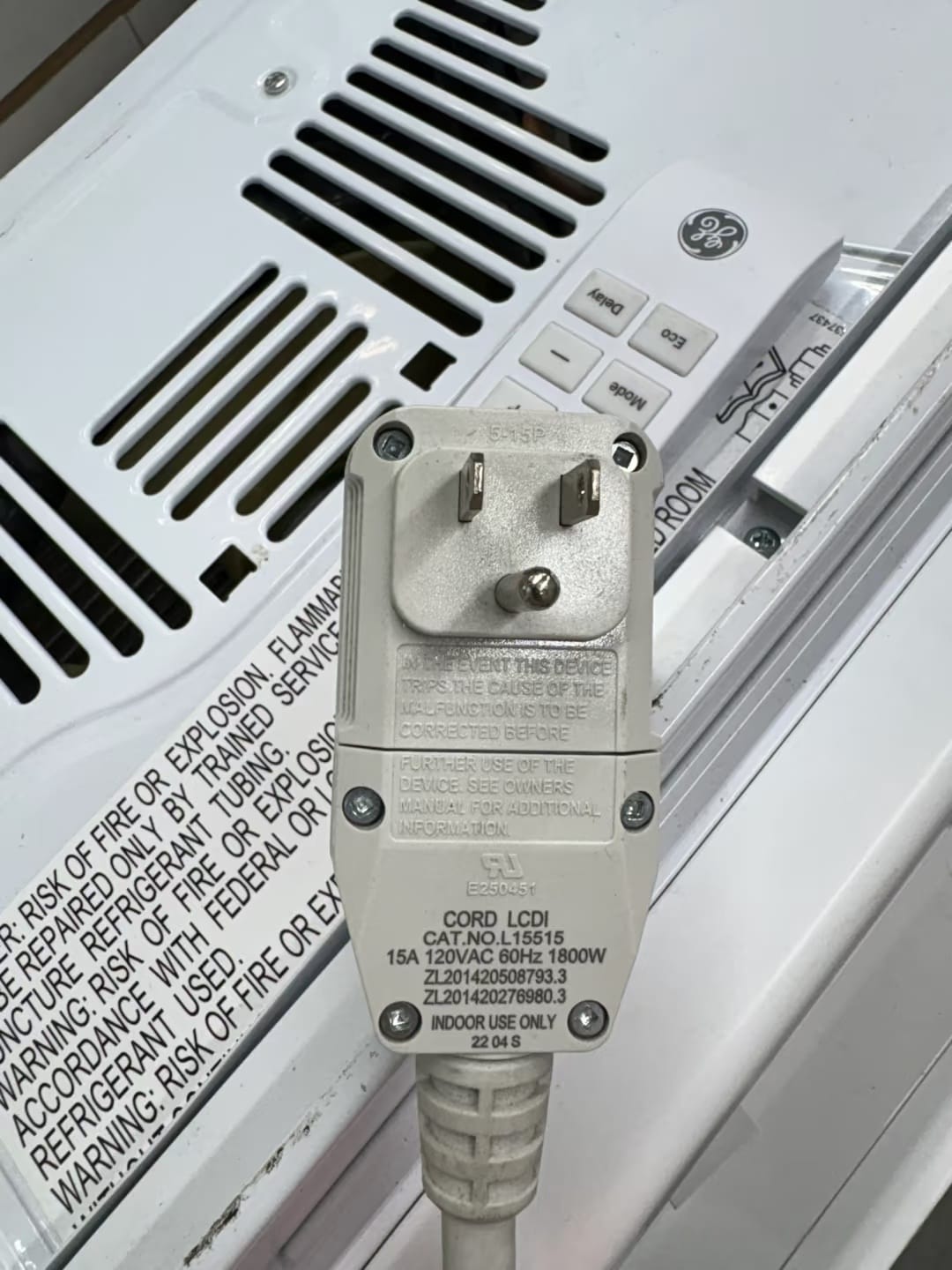
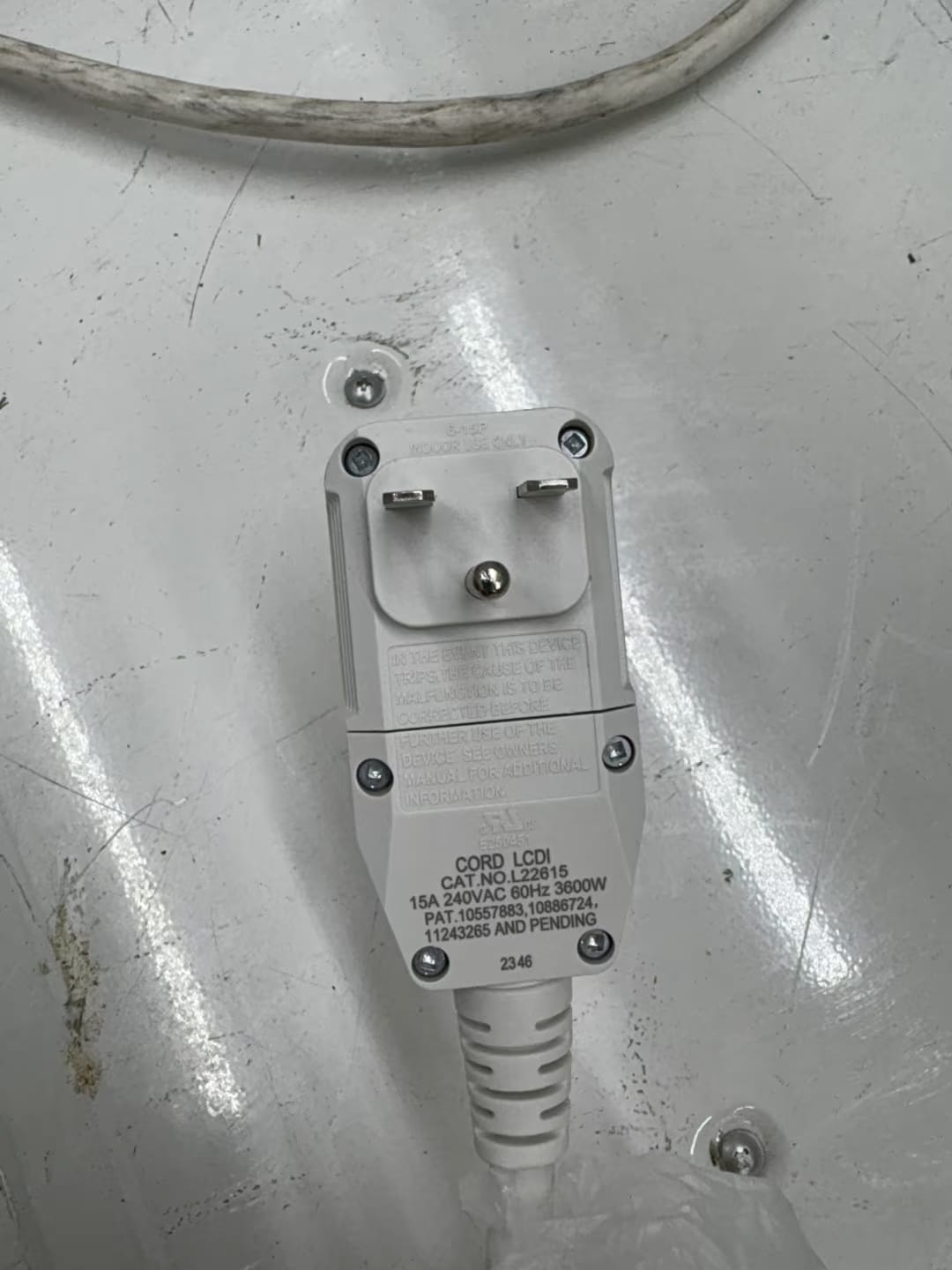


3. Read the Appliance Label
Every appliance is required to list its input voltage. Look for wording like:
- “Input: 120V ~ 60Hz” → safe for standard outlets
- “Input: 240V ~ 60Hz” → requires a special 240V circuit
You can usually find this label on the back of the unit, near the power cord, or inside the user manual. This step is especially useful for things like window A/C units or imported appliances where the plug might not give away the voltage.
With just these three checks—outlet shape, plug size, and label—you’ll be able to identify outlet voltage with confidence, without needing to open the breaker panel or touch wiring.
When You’ll Typically See 240 V Outlets
If you walk through a typical U.S. home, you’ll see dozens of 120V outlets—but only a few 240V outlets. That’s because they’re reserved for appliances that need a lot more power than a standard plug can provide.
Here are the most common places you’ll run into them:
- Laundry rooms – Electric dryers almost always need 240V. If you’re asking yourself, “Does my dryer need 240V?” the answer is likely yes—unless it’s a compact or gas-powered model.
- Kitchens – Large ovens, cooktops, and some built-in microwaves require 240V to handle heating elements.
- Garages – EV chargers are becoming more popular, and nearly all Level 2 chargers require a 240V circuit.
- Outdoors/utility areas – Central A/C compressors, heat pumps, and well pumps typically run on 240V.
Pro Tip: Look at the Breaker Panel
If you want further confirmation, your breaker panel can provide clues:
- Single-pole breaker → 120V circuit
- Double-pole breaker → 240V circuit
Double-pole breakers connect to both hot wires in the split-phase system and are commonly labeled for appliances like dryers, ranges, or A/C units.
Safety reminder:
It’s okay to open the panel door and look—but do not remove covers or touch wiring unless you’re qualified.
When in doubt, take a photo and consult a licensed electrician.
Can You Convert a 120V Outlet to 240V?
Homeowners often wonder: can you convert 120V to 240V if you don’t already have the right outlet? The short answer is yes—but it’s not as simple as swapping out the receptacle.
Why It’s Not a DIY Job
A 240V circuit requires:
- Two hot wires instead of one
- A double-pole breaker in your panel
- Correct wire gauge to handle the increased load
That means converting an outlet involves rewiring from the breaker panel and ensuring everything meets code. Attempting this on your own without proper training can result in fire hazards, code violations, or damaged appliances.
Typical Costs
The cost to install a 240V outlet varies depending on how far the outlet is from the electrical panel, whether your panel has room for another breaker, and whether permits are required. On average, homeowners spend:
- $250–$400 for a simple installation near the panel
- $500–$1,000+ if new wiring must be run across multiple rooms or to a detached garage
If you’re planning for a future EV charger, heat pump, or large appliance upgrade, it’s wise to install the 240V outlet sooner rather than later.
Best Practice
Always hire a licensed electrician. Not only will the work be safer, but it also ensures your installation passes inspection and complies with the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Why Confirming Voltage Matters Before Installation
Knowing whether an outlet is 120V or 240V isn’t just a technical detail.
It directly affects:
- Appliance compatibility
- Installation safety
- Upgrade planning (EV chargers, heat pumps, electric heating)
- Whether professional work is required
Many installation problems happen not because the appliance is faulty—but because the electrical setup was misunderstood.
Not Sure What Your Setup Supports?
If you’re planning to install or upgrade high-power equipment and aren’t fully confident in your home’s electrical capacity, the next step isn’t buying hardware—it’s understanding your system as a whole.
👉 Learn how homeowners plan electrical capacity and appliance upgrades safely:
→ Home Electrical & Energy Planning Guide
Conclusion: Quick Takeaways
- 120V outlets power everyday devices
- 240V outlets support heavy-duty appliances
- You can identify voltage by outlet shape, plug design, or appliance labels
- When uncertain, professional confirmation is the safest option
A few minutes of checking now can prevent costly mistakes later.
FAQ
Can a standard outlet be both 120V and 240V?
No. They are wired differently and designed with distinct outlet shapes to prevent accidents. A receptacle is always one or the other.
Is it safe to test with a multimeter?
Yes, but only if you’re experienced. A non-contact voltage tester for home outlets is safer for beginners. When in doubt, leave it to an electrician.
Do smart plugs tell you voltage?
Most smart plugs don’t measure voltage directly. They can show energy usage for 120V devices, but for full-circuit monitoring—including 240V appliances—you’ll need a smart energy monitor.
What happens if you plug 120V into 240V?
It can destroy the device instantly. This is why 120V 240V outlet safety matters so much—appliance plugs and outlets are purposely designed not to fit each other.
Does my dryer need 240V?
Most full-size electric dryers in the U.S. do require 240V. Compact dryers and gas dryers may only use 120V, so always check the label before buying or installing.