In today's hyper-connected age, home energy management is no longer just a buzzword; it is an essential framework guiding how households optimize their power consumption. With the advent of smart energy solutions, breakthroughs in IoT-based energy systems, and the increasing push for renewable energy integration, the entire sector is evolving at an unprecedented pace. This evolution is being further propelled by growing awareness of energy efficiency measures, making modern homes not only more environmentally responsible but also more cost-effective. In this in-depth guide, we will explore the foundational concepts, technologies, market trends, and challenges of home energy management. We will also discuss how consumers and industry players can collaborate to shape a more sustainable and intelligent energy future.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), residential buildings account for nearly 25% of global electricity consumption. This staggering figure underscores the critical importance of adopting efficient home energy management systems. As the demand for electricity continues to rise—especially in rapidly developing regions—there is a corresponding surge in greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing comprehensive home energy strategies not only reduces carbon footprints but also delivers tangible cost savings to consumers.
The growing popularity of renewable energy integration like solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems is empowering homeowners to produce and store clean energy. On the other hand, smart energy solutions fueled by IoT-based energy systems allow real-time monitoring and control of various household devices. By combining renewables with intelligent control, homeowners can optimize energy usage, slash utility bills, and minimize their environmental impact.
Why It Matters
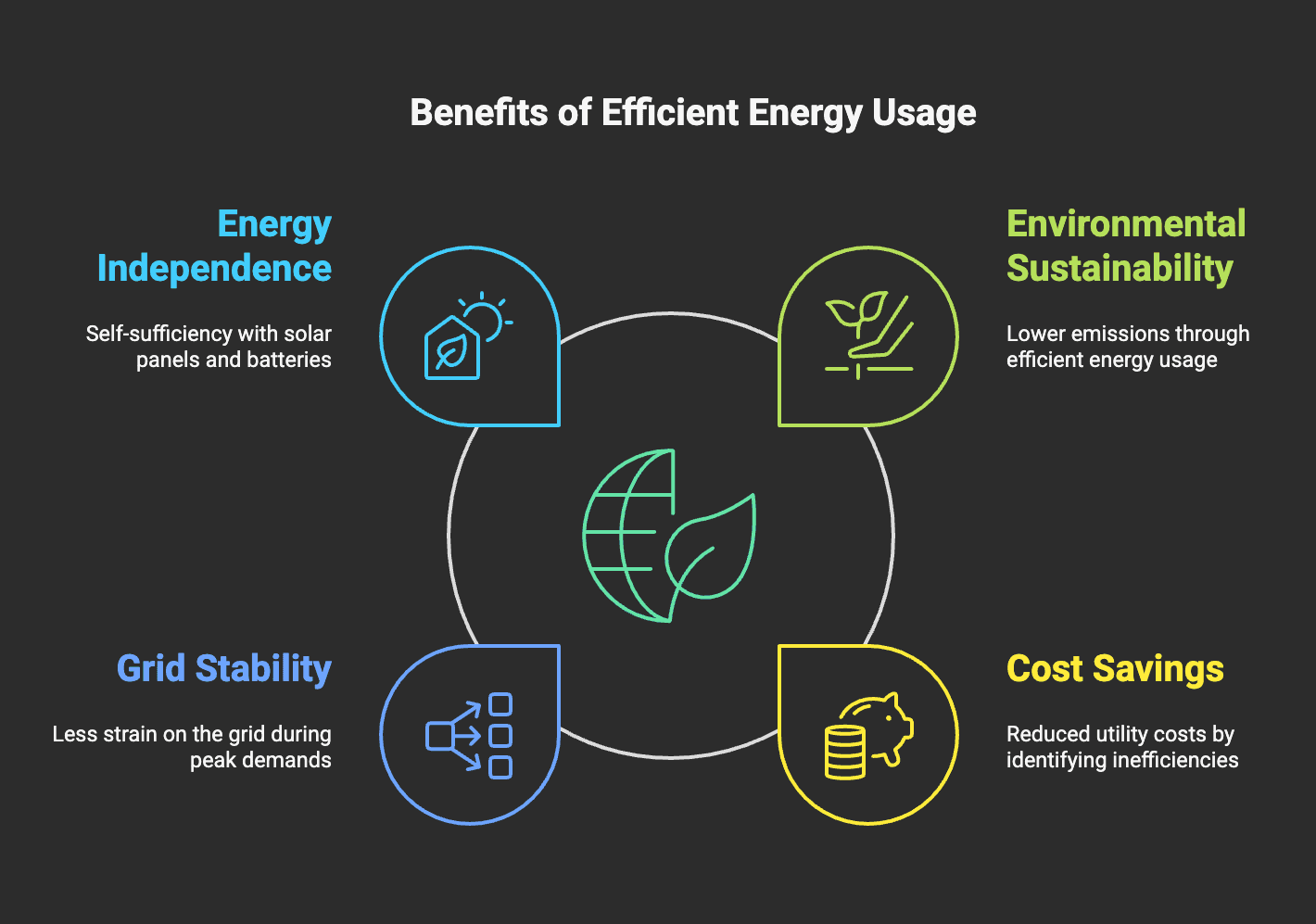
- Environmental Sustainability: Efficient energy usage directly translates to lower emissions.
- Cost Savings: Monitoring energy consumption identifies inefficiencies and reduces utility costs.
- Grid Stability: Well-managed households put less strain on the electrical grid, helping balance peak demands.
- Energy Independence: Homes equipped with solar panels and batteries can achieve partial or total energy self-sufficiency.
Key Technologies Transforming Energy Management
Smart Meters and Real-Time Monitoring
Smart meters are the backbone of home energy management. These devices provide real-time data on electricity consumption, enabling homeowners to track usage patterns and identify wasteful behaviors. Utility companies also benefit by accessing granular data, which helps in load balancing and planning.
- Features:
- Interval metering (e.g., 15-minute intervals)
- Two-way communication with utility providers
- Remote firmware updates
- Advantages:
- Immediate consumption insights
- Automated billing and reduced manual meter reading
- Potential for dynamic pricing models (time-of-use rates)
In some regions, governments and energy companies offer subsidies or rebates for installing smart meters, making it an attractive proposition for cost-conscious homeowners.
Solar Energy and Storage Systems
Renewable energy integration has gained significant traction over the past decade, with solar photovoltaic (PV) installations topping the list of environmentally friendly solutions. By pairing solar panels with energy storage systems (ESS) such as lithium-ion batteries, households can capture surplus energy generated during peak sunlight hours and use it later—especially during evenings or periods of high demand.
- Photovoltaic Panels: Convert sunlight directly into electricity.
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS): Store excess solar energy for off-peak consumption.
- Inverters: Convert direct current (DC) from solar panels to alternating current (AC) used in homes.
Financial and Environmental Impact
- Return on Investment (ROI): Though the initial installation cost can be high, declining solar panel prices and various tax incentives accelerate ROI.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Each kilowatt-hour (kWh) of solar-generated power offsets a corresponding kWh from fossil fuels.
According to BloombergNEF, the cost of solar PV modules has dropped by over 80% since 2010, making it an increasingly viable solution for many homeowners seeking energy efficiency gains.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G)
Another exciting innovation is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, where electric vehicles (EVs) act as mobile energy storage units. EVs can store energy during low-demand periods (usually at night) and release it back to the grid or to the home during peak hours. This dynamic use of EV batteries ensures a more stable grid while providing an additional revenue or cost-saving stream for EV owners.
- Bi-Directional Charging: Allows energy flow from the car to the grid and vice versa.
- Smart Integration: IoT-based controllers decide the optimal time to charge or discharge based on real-time grid signals and electricity pricing.
- Peak Shaving: Reduces strain on the grid during high-demand periods.
AI and Machine Learning in Energy Optimization
Modern home energy management systems frequently incorporate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms to analyze consumption patterns and weather forecasts. With these insights, they predict future energy usage and automatically optimize system performance.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models can forecast daily or weekly energy needs based on historical data and real-time inputs like temperature and humidity.
- Adaptive Control: Machine learning algorithms adjust energy settings dynamically, ensuring minimal waste.
- Fault Detection and Diagnostics: Automatically identifies anomalies in equipment performance (e.g., malfunctioning HVAC systems) and notifies homeowners or service providers.
By harnessing AI-driven insights, homeowners can reduce energy waste by up to 20%, according to a study published in the Journal of Cleaner Production.
Market Trends and Global Outlook
Growth in Residential Solar
The adoption of residential solar is skyrocketing globally. Wood Mackenzie forecasts that the U.S. residential solar market alone will add up to 3 gigawatts of capacity annually by 2025. Similar expansions are evident in Europe, Australia, and parts of Asia, reflecting a collective shift towards renewable energy integration and smart energy solutions.
Adoption Rates of Smart Solutions
- North America: High uptake of intelligent thermostats (e.g., Nest, Ecobee), creating a fertile market for more advanced IoT-based energy systems.
- Europe: Policies like the European Green Deal are accelerating the deployment of smart meters and distributed energy resources (DERs).
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization and robust smartphone penetration are driving interest in home energy management, though regulatory frameworks vary significantly across countries.
Economic Incentives and Policy Shifts
Government incentives play a pivotal role in promoting home energy management. Tax rebates, net metering programs, and low-interest financing plans encourage the adoption of renewable energy integration systems. For instance, the U.S. Investment Tax Credit (ITC) provides a 26% tax credit for residential solar installations. Similar or even more generous incentives can be found in countries like Germany, Australia, and Japan.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Single-Family Homes
Case Study: A suburban household in California installed a home energy management system that integrates a rooftop solar array with a battery pack. Through real-time data analysis, the system schedules high-energy tasks (e.g., running the dishwasher or washing machine) during peak solar generation. As a result, the family reduced their annual electricity bill by nearly 40% and even received credits from the utility for feeding surplus power back into the grid.
Key Takeaways:
- Optimized scheduling reduces peak load charges.
- Integration of battery systems provides backup power during outages.
- Real-time monitoring and automation enhance overall user experience.
Community-Level Microgrids
Community microgrids represent an advanced step toward localized energy independence. In certain neighborhoods, multiple homes share a collective microgrid, pooling resources like solar panels and battery banks. A central control system distributes power efficiently among the homes while also managing grid interconnections.
Example: A pilot project in Brooklyn, New York, uses blockchain-based technology to facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading among neighbors with rooftop solar. Residents can buy and sell excess energy within the local community, significantly reducing reliance on conventional utility services.
Benefits:
- Enhanced resiliency during large-scale blackouts.
- Localized control reduces transmission losses.
- Potential for innovative billing models (P2P energy trading).
Challenges in Deploying Home Energy Management Systems
Despite the clear advantages of smart energy solutions and IoT-based energy systems, several obstacles remain.
Security and Data Privacy
The sheer volume of data generated by home energy management systems raises significant privacy concerns. Personal usage patterns could be exploited if not properly secured. A robust cybersecurity framework is crucial to protect sensitive data from potential hacking or unauthorized access.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Manufacturers often develop proprietary communication protocols and platforms, hindering seamless integration among different devices. For a homeowner looking to install a new solar inverter, battery system, or EV charger from various brands, ensuring interconnectivity can be a formidable challenge.
Equipment Reliability and Maintenance
While advanced IoT sensors and devices offer unprecedented control and monitoring, they also introduce new points of failure. Routine maintenance of smart meters, inverters, or battery systems becomes critical to ensure uninterrupted energy efficiency gains.
Standardization of Communication Protocols
Energy management solutions must talk to each other in a standardized manner for effective orchestration. Organizations like the OpenADR Alliance and the Zigbee Alliance are working on open standards, but universal adoption is yet to be realized. Until consistent protocols are established, interoperability remains an uphill battle.
Proven Solutions and Emerging Opportunities
Leveraging 5G and Edge Computing
Next-generation networks like 5G promise low-latency connections and higher data throughput, crucial for real-time energy management. Additionally, edge computing—processing data closer to the source rather than on centralized cloud servers—enhances response times and reduces bandwidth usage.
- Local Decision Making: Smart inverters or thermostats can make split-second decisions without waiting for cloud-based commands.
- Network Efficiency: Edge computing offloads data processing, reducing traffic on central servers.
- Enhanced Security: Local encryption and data storage minimize the risk of massive data breaches.
Policy and Consumer Awareness
As climate change impacts become more evident, the political and social will to embrace home energy management grows stronger. Many governments are ramping up investments in grid modernization and offering rebates for renewable energy integration. Homeowners, in turn, are becoming more aware of the cost benefits of energy efficiency—not just for the planet but for their wallets as well.
Visual Overview: Energy Flow and Systems Architecture
Below is a simplistic Mermaid flowchart illustrating a typical home energy management setup:
flowchart LR A[Smart Meter] --> B[Home Energy Management Controller] B --> C[Appliances & HVAC] B --> D[Battery Storage] B --> E[EV Charging Station] D --> F[Renewable Source: Solar Panels] E --> G[Grid V2G] F --> B G --> A
Legend:
- Smart Meter: Feeds consumption and production data to the Home Energy Management Controller.
- Appliances & HVAC: End-use systems that draw power from the controller.
- Battery Storage & Renewable Sources: Provide and store clean energy.
- EV Charging Station & Grid V2G: Connects electric vehicles to the grid, enabling two-way energy transfer.
Comparative Analysis of Popular Smart Energy Solutions
To understand the market better, let’s look at a brief comparison table showcasing various solutions and their key features:
| Solution | Primary Function | Notable Features | Approx. Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nest Thermostat | Smart HVAC Control | Remote access, AI auto-scheduling | $129 - $249 |
| Tesla Powerwall | Battery Storage System | High-capacity Li-ion cells, backup power, real-time monitoring | $7,500 - $9,000 (excluding installation) |
| SolarEdge Inverter | Solar Energy Optimization | MPPT technology, module-level monitoring | $1,000 - $2,000 |
| Enphase IQ8 | Microinverter for Solar PV | Improved safety, real-time data, modular design | $150 - $200 per module |
| Wallbox Quasar | Bi-Directional EV Charger | V2G support, smart scheduling | $4,000 - $5,000 |
Notes:
- Costs vary depending on region, installation charges, and regulatory incentives.
- Features like IoT-based energy systems integration and advanced analytics may come at an additional subscription fee.
Future Outlook: Towards Fully Integrated IoT-Based Energy Systems
As IoT technologies mature, the vision of a fully autonomous home energy management ecosystem moves closer to reality. The integration of big data analytics, 5G, and AI will allow for instantaneous adjustments to consumption and storage, while advanced battery chemistries (such as solid-state batteries) could dramatically enhance storage capacity and safety.
Potential Breakthroughs
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells for residential backup power.
- Blockchain for secure peer-to-peer energy trading.
- Digital Twins for simulated energy usage scenarios, reducing real-world trial and error.
Longer-Term Implications
- Decentralized Energy Grids: The rise of microgrids and prosumers (producers + consumers) will reshape the traditional utility model.
- Sustainable Communities: Future smart cities will incorporate large-scale IoT-based energy systems that optimize residential and commercial power usage simultaneously.
- Data-Driven Policies: Governments may rely on real-time consumption data to craft more dynamic energy regulations, rewarding energy efficiency in a transparent manner.
As we stand on the cusp of an energy revolution, home energy management is rapidly becoming a central topic in discussions around smart energy solutions. From IoT-based energy systems that provide real-time insights to advanced battery technologies that enable renewable energy integration, the potential for more intelligent and sustainable household power usage is enormous. Yet, to fully realize this potential, policymakers, technology providers, and end-users must collaborate on standardization, cybersecurity, and equitable incentive programs.
Investments in research and development, alongside the proliferation of edge computing and 5G, herald a near future where our homes not only become self-sufficient but also actively contribute to a more resilient and stable power grid. By embracing energy efficiency measures and fostering innovation in renewable energy integration, we can collectively take a significant step towards mitigating the looming threats of climate change while simultaneously ensuring energy affordability and reliability.
The journey has begun, and the blueprint is taking shape. The question is no longer “if” but “how quickly” these technologies will transform our households into sustainable, intelligent power hubs. For consumers, adopting a home energy management system is not just an eco-conscious choice—it’s also a wise investment in long-term cost savings, self-reliance, and the creation of a greener planet for future generations.