Alternating Current (AC) power supply is the standard method for delivering electricity to homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. The voltage levels and phase configurations differ depending on the application. In this article, we will:
✅Explain the waveform characteristics of 120V single-phase, 120V/240V split-phase, and 120V/208V three-phase systems
✅各システムの正弦波電圧波形を図解する
✅さまざまな構成で電圧計算がどのように実行されるかを示します
1. 120V単相交流波形
🔹一般的に使用される用途:
✔ 標準的な家庭用コンセント
✔ 照明回路
✔ 小型家電
特徴:
- RMS電圧:120V
- ピーク電圧の計算:
$$V_{\text{peak}} = V_{\text{RMS}} \times \sqrt{2} = 120V \times 1.414 = 170V$$ - 頻度:60Hz(16.67msごとに1サイクル)
- 電圧は+170Vと-170Vの間で振動します
次の図は、120V AC正弦波:
2. 120V/240V分相交流波形
🔹一般的に使用される用途:
✔ 住宅用電気システム
✔ 高出力家電(電気オーブン、HVAC、給湯器、EV充電器)
仕組み:
- センタータップ付きトランスは2本のホットワイヤ(L1とL2)と1本のニュートラルワイヤ(N).
- L1 からニュートラル (120V)、L2 からニュートラル (120V)、および L1 から L2 (240V)。
- L1とL2は180°位相がずれているつまり、波形は正反対になります。
240Vの電圧計算:
$$V_{\text{peak}} = 240V \times \sqrt{2} = 339V$$
下の図は、120V/240V分相正弦波:
3. 120V/208V 三相スター交流波形
🔹一般的に使用される用途:
✔ 商業ビル
✔ 集合住宅
✔ データセンターとITインフラストラクチャ
仕組み:
- A三相Y字型変圧器提供するL1、L2、L3、ニュートラル(N).
- 各相から中性線(L1-N、L2-N、L3-N)までの電圧は 120V です。
- 各位相ペア (L1-L2、L2-L3、L1-L3) は、120° の位相シフトにより 208 V になります。
208Vの電圧計算:
$$V_{\text{L1-L2}} = V_{\text{L1-N}} + V_{\text{L2-N}} = 120V + 120V = 240V$$
$$V_{\text{Line}} = V_{\text{Phase}} \times \sqrt{3} = 120V \times 1.732 = 208V$$
下の図は、120V/208V 三相Y字正弦波:
4. 電圧波形の可視化
以下は、以下の波形をプロットしたものです。120V単相、120V/240V分相、および120V/208V三相交流システム.
📌グラフからの主な観察事項:
- 120V単相:1つの正弦波が振動する+170Vおよび-170V.
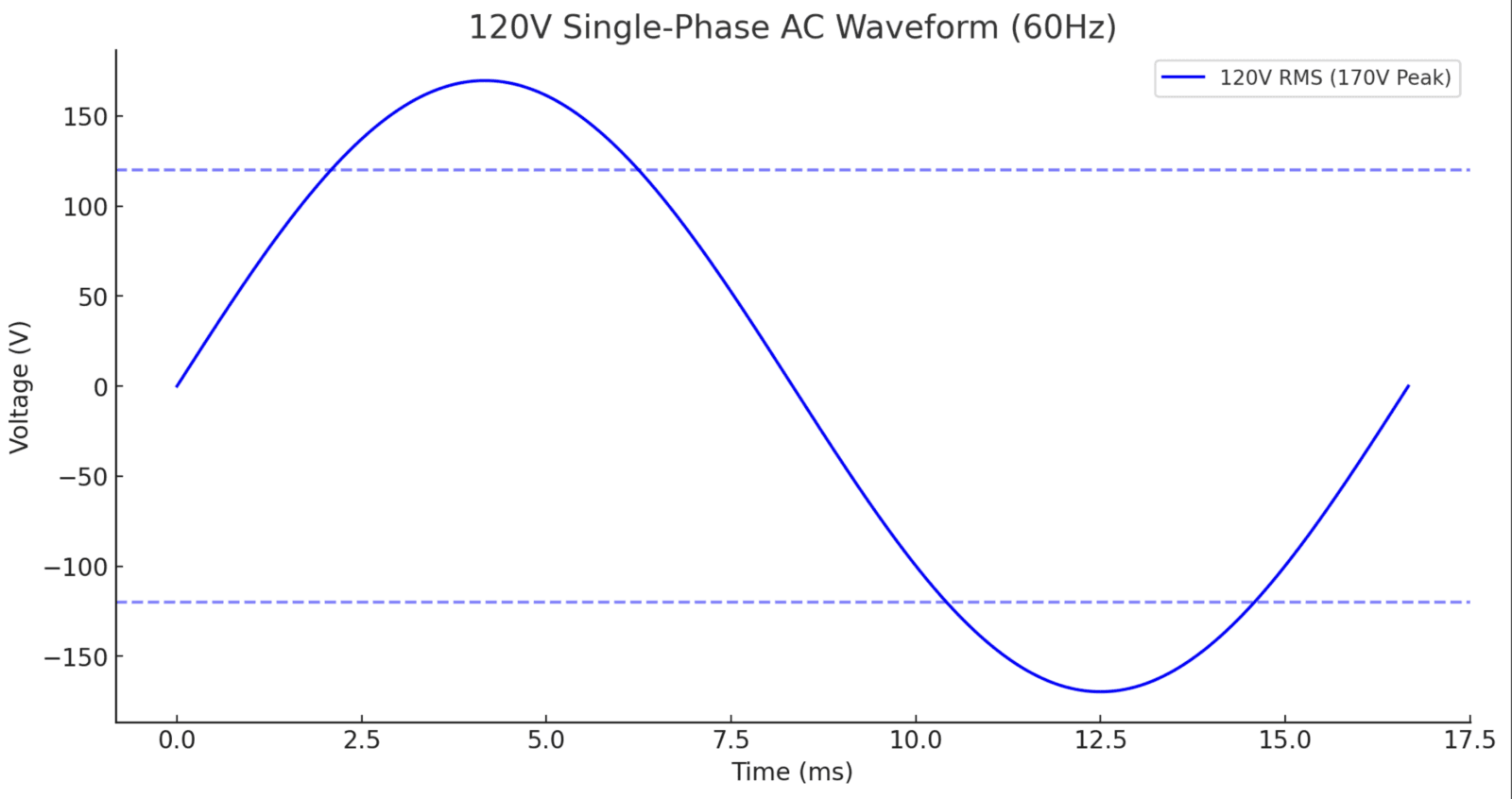
- 標準的な家庭用コンセント、60Hz、正弦波、ピーク電圧170V.
- AC周期は16.67ms(1/60Hz)です。
- 120V/240V スプリットフェーズ:L1とL2は180°位相がずれている、生産L1-L2間に240V.
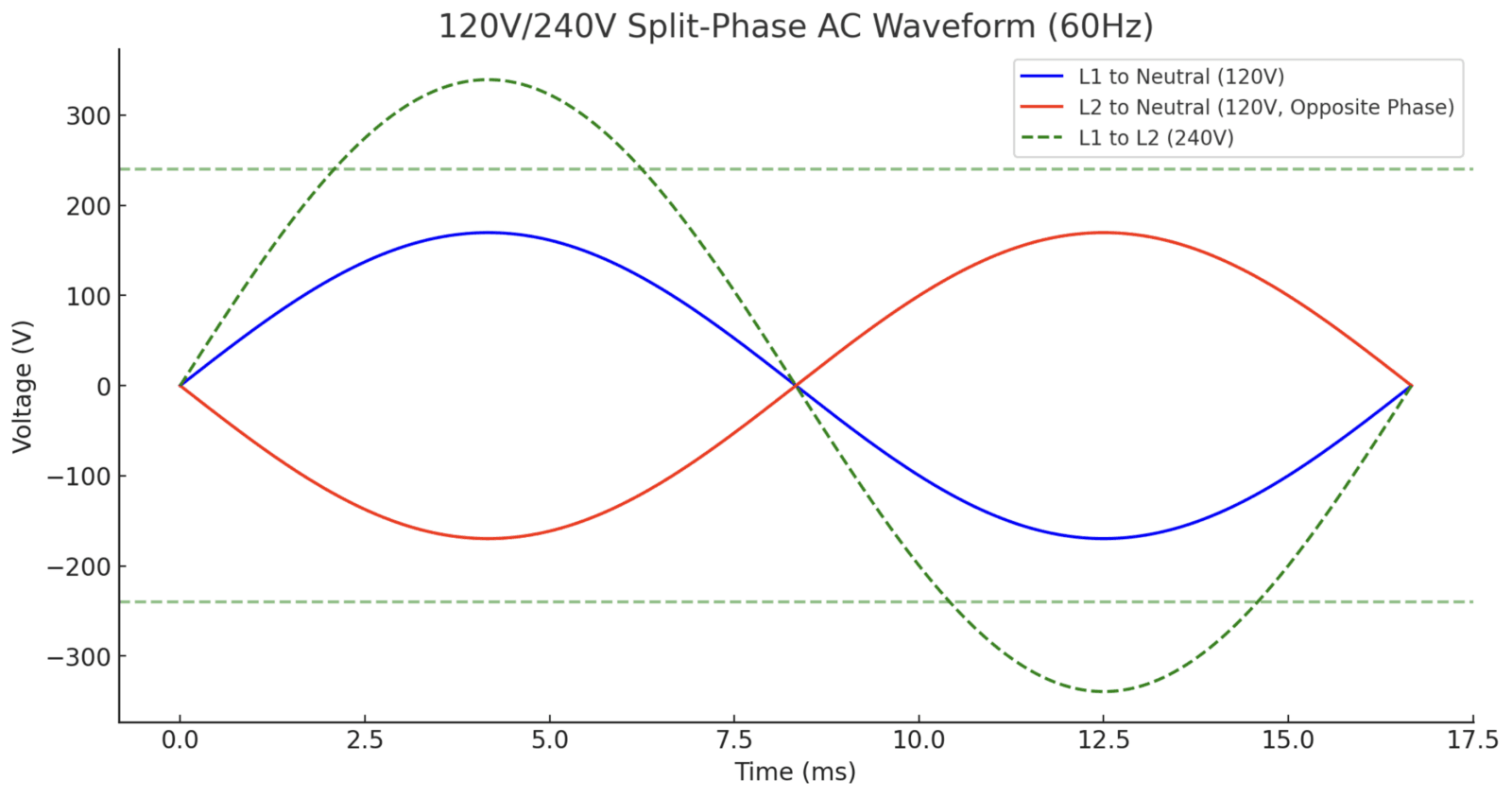
- L1とL2は180°異なるため、240Vの差動電圧が発生します。.
- L1→NとL2→Nは両方とも120Vで、L1→L2は240V電源高出力デバイス(EV充電器、エアコンなど)向け。
- 120V/208V 三相スター:L1、L2、L3は120°離れた、 形にする任意の2相間で208V.
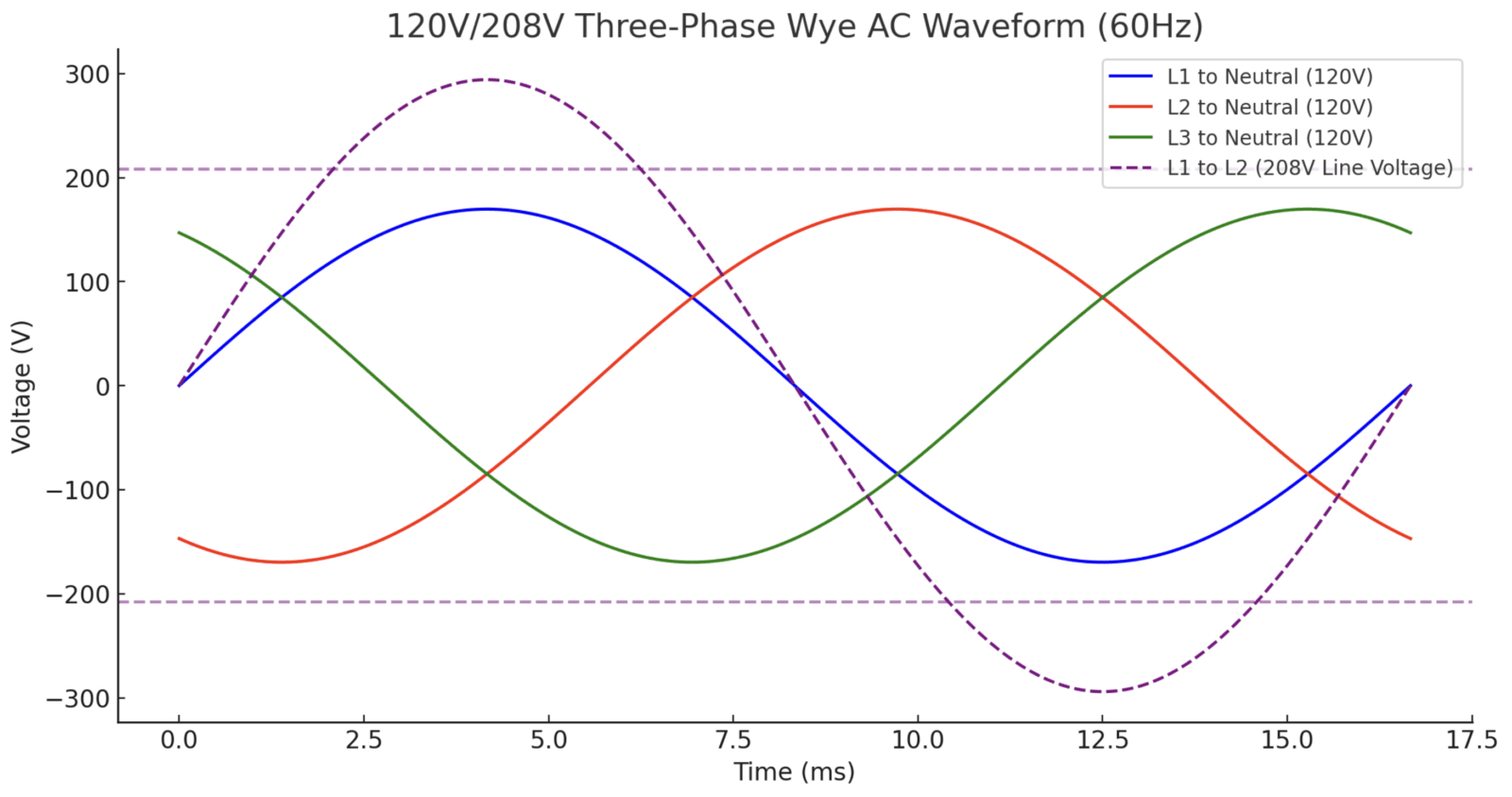
- L1、L2、L3は120°異なります.
- L1、L2、L3 → ニュートラル = 120V単相負荷(照明、オフィス機器)用。
- L1 → L2, L2 → L3, L1 → L3 = 208V三相負荷(モーター、商用 HVAC)用。
5. 電圧波形を理解することがなぜ重要なのか?
AC電圧波形を理解することは、電気システムの設計、負荷のバランス調整、エネルギー効率の向上.
💡実用的なアプリケーション:
✔住宅所有者と電気技師– 家電製品に適した電圧を選択する
✔事業主– 商業スペースにおけるエネルギー効率の最適化
✔データセンターと工場– バランスの取れた三相電力配分の確保
🔹適切なスマートエネルギーモニターの選択:
| スマートメーター | 最適な用途 | 対応電圧システム |
|---|---|---|
| WattNet-3 | 一般的な三相エネルギー監視 | 120/208V、277/480V 三相(スター) |
| WattPanel-3X | 高度なマルチチャネル負荷監視 | 120/208V、277/480V 三相 |
📌Monitoring voltage and current waveforms with smart meters ensures optimal energy distribution and cost savings.
6. 結論:電圧システムに基づくエネルギー使用の最適化
理解120V、120V/240V、120V/208Vの波形より良い負荷分散、エネルギー効率、電気システム設計.
✅重要なポイント:
- 120V単相:家庭用コンセントや小型家電の規格です。
- 120V/240V スプリットフェーズ:住宅の高電力負荷に使用されます。
- 120V/208V 三相:商業ビルでよく見られ、電力を効率的にバランスさせます。
🚀 **エネルギー監視をアップグレードするにはGrusスマートメーター今日!