Um guia sobre a ciência por trás da detecção de gás — e a tecnologia de segurança que protege sua casa.
Uma ameaça oculta que você não pode ver nem sentir o cheiro.
Um vazamento de gás é um daqueles perigos que permanecem invisíveis até que seja quase tarde demais.
Natural gas is odorless by nature, and although suppliers add a sulfur-like scent so you can smell it, most leaks start too small for human senses to notice. A simple spark — from a switch, a stove, or even static — can trigger disaster.
É por issoalarmes de vazamento de gásexist. They quietly monitor the air every second, detecting combustible gases before they reach dangerous levels. But many people still wonder:Como esses dispositivos funcionam na prática?
Let’s take a closer look at the technology, logic, and smart systems that make modern gas detection possible.
Entendendo os alarmes de vazamento de gás — O que eles realmente detectam?
Adetector de vazamento de gásnão é o mesmo que umalarme de monóxido de carbono (CO).
Os alarmes de CO detectam gases tóxicos, enquanto os detectores de vazamento de gás identificam...gases inflamáveiscomo o metano (gás natural), o propano ou o butano, que podem causar explosões.
Tipos de detectores de gás
- Detectores de gás natural (metano)– Instalado próximo ao teto, pois o metano sobe.
- Detectores de propano ou GLP– Deve ser colocado perto do chão, já que o propano é mais pesado que o ar.
- Detectores multigás– Combinar sensores para gases combustíveis e tóxicos.
Cada tipo desempenha um papel num contexto mais amplo.sistema de alarme de gás natural, frequentemente associado a válvulas de corte ou ventiladores.
Por dentro da tecnologia — Como funcionam os alarmes de vazamento de gás
Quando você conecta um alarme de vazamento de gás, ele silenciosamente começa a fazer uma coisa —farejando o ar.
Mas o que acontece dentro desse pequeno dispositivo?
Em sua essência, a maioria dos alarmes de gás residenciais usasensores semicondutores—minúsculos chips eletrônicos que reagem ao gás no ar alterando seu sinal elétrico.Este processo é a essência doprincípio de funcionamento do detector de gás: when gas is present, the sensor’s electrical resistance shifts, and the alarm reacts if it crosses a danger level.
Esses sensores semicondutores são normalmente feitos dedióxido de estanho (SnO₂). In normal air, oxygen molecules attach to the sensor’s surface, capturing electrons and keeping resistance high. When gases like methane or propane enter, they react with those oxygen ions, releasing the electrons and lowering resistance.
Essa mudança é medida instantaneamente. Assim que ultrapassa um limite predefinido — geralmente cerca de 10% do gás —limite inferior de explosividade (LIE)—o microcontrolador aciona o alarme.
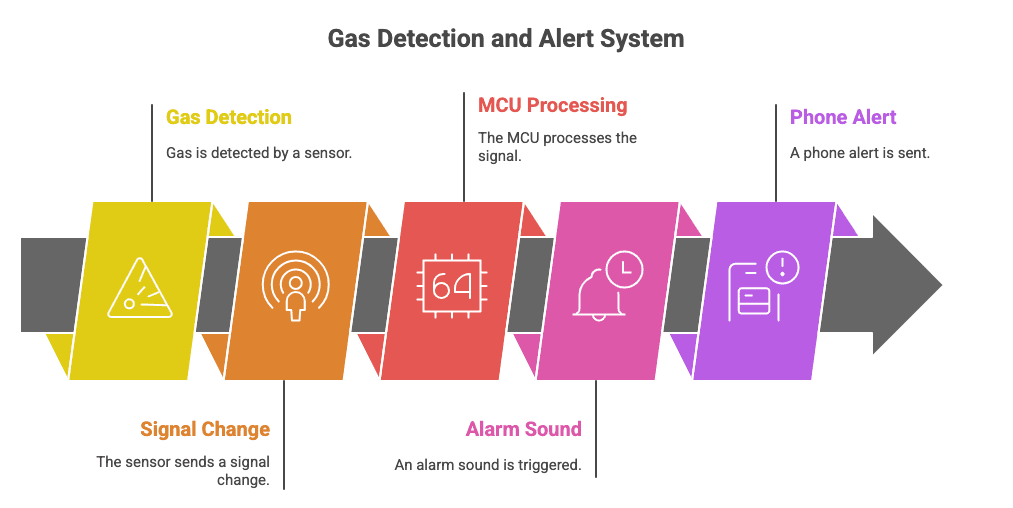
A sequência de segurança
- O gás entra na câmara do sensor.
- O chip de detecção registra as mudanças de resistência.
- O circuito processa o sinal.
- O alarme emite um sinal sonoro (85 dB) e pisca.
- Se estiver conectado ao Wi-Fi, uma notificação push será enviada para o seu celular.
Isso éComo funcionam os alarmes de vazamento de gás— traduzindo reações químicas no ar em alertas eletrônicos instantâneos.
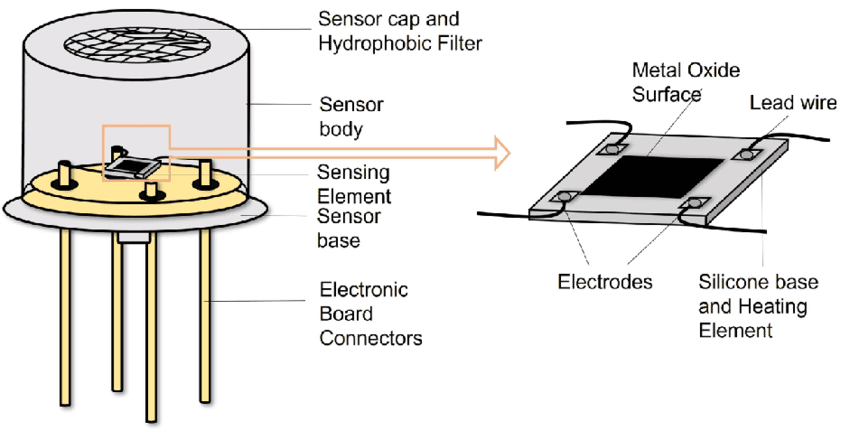
Tipos de sensores de gás combustível explicados
Nem todos os detectores detectam gás da mesma maneira. Veja como diferentes tecnologias de sensores se comparam:
1. Sensores semicondutores (SnO₂) — Confiáveis e acessíveis
- Princípio:Pequenos chips detectam alterações na resistência causadas pela exposição ao gás.
- Prós:Resposta rápida, compacto, baixo custo.
- Contras:Sensível à umidade, com deriva gradual ao longo do tempo.
- Melhor para:Cozinhas residenciais, apartamentos, imóveis para alugar.
Think of them as the “smoke alarm equivalent” for gas — compact, inexpensive, and always on guard.
2. Sensores de Combustão Catalítica — Resistência Industrial
- Princípio:O gás queima em uma esfera catalisadora, produzindo calor que altera a resistência.
- Prós:Muito preciso em níveis elevados de gás.
- Contras:Necessita de oxigênio; maior consumo de energia.
- Melhor para:Cozinhas comerciais ou fábricas.
3. Sensores infravermelhos (IV) — Precisos, mas caros
- Princípio:Mede a capacidade do gás de absorver luz infravermelha.
- Prós:Imune a envenenamento, longa expectativa de vida.
- Contras:Caros; módulos maiores.
- Melhor para:Ambientes industriais ou de laboratório.
| Tipo de sensor | Método de detecção | Sensibilidade | Custo | Caso de uso |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semicondutor | Mudança de resistência | Alto | Low | Alarmes residenciais |
| Pérola catalítica | Calor de combustão | Médio | Médio | Industrial |
| Infravermelho (IV) | Absorção de luz | Muito alto | Alto | Comercial |
O que acontece quando um vazamento é detectado?
When gas levels rise above the preset limit, the alarm’s internal chip immediately triggers an alert:
- Acionar:O sinal do sensor ultrapassa o limite.
- Alerta sonoro:Buzzer com volume acima de 85 dB e luz intermitente.
- Alerta inteligente:As versões com Wi-Fi enviam notificações através do aplicativo.
- Automação:Os sistemas interligados acionam uma válvula de corte ou um ventilador.
💡Dica profissional:Pair your alarm with a Smart Gas Shutoff Valve — it can automatically stop gas flow the moment a leak is detected.
Integração inteligente de Wi-Fi — Segurança que acompanha você aonde quer que vá.
Os detectores tradicionais apenas fazem barulho.
Alarmes inteligentes com Wi-Fi vão além — elesmensagem para você instantaneamenteRegistrar dados e conectar-se a outros dispositivos inteligentes, como ventiladores de exaustão ou assistentes de voz.
É assim que umsistema de alarme de gás naturaltorna-se uma verdadeira rede de segurança.
Dicas de instalação — Como funciona um detector de vazamento de gás em sua casa?
- Metano / Gás natural:Instale próximo ao teto (12–24 polegadas abaixo).
- Propano / GLP:Próximo ao chão (a menos de 30 cm acima).
Evite janelas, saídas de ar ou fogões.
Faça o teste mensalmente e substitua após 5 a 7 anos para obter a melhor precisão.
Por que toda casa precisa de um alarme de vazamento de gás
You wouldn’t wait for a fire to buy a smoke alarm — don’t wait for a gas incident to install a gas detector.
Mesmo um pequeno vazamento pode causar fadiga, tontura ou explosões.
Adetector inteligente de vazamento de gásOferece alerta antecipado e controle remoto, proporcionando segurança mesmo quando você não está em casa.
Protect your home from both gas and carbon monoxide leaks with our dual smart detector set. EnjoyAté 10% de descontoPor um tempo limitado — a tranquilidade nunca foi tão acessível.
Compre o Pacote Black Friday →P1: Como um alarme de vazamento de gás detecta gás combustível?
Ele usa um minúsculochip sensor semicondutorthat reacts when gases like methane or propane contact its surface. The chip’s electrical signal changes as gas concentration rises, and the circuit sounds the alarm once the level exceeds a safe threshold.
Q2: Quais gases um detector doméstico consegue identificar?
A maioria detectagases inflamáveis— metano (gás natural), propano e butano. Alguns modelos também detectam hidrogênio. Paragases tóxicosAssim como para monóxido de carbono, use um alarme de CO específico, como oGasNet-CM.
P3: Qual a precisão desses detectores?
Os sensores semicondutores modernos detectam quantidades tão pequenas quanto200–500 ppmof gas and react within seconds. Accuracy can decline after 5–7 years, so regular replacement is essential.
Q4: Onde devo instalar um?
Montedetectores de gás natural perto do teto, edetectores de propano perto do chãoPara obter leituras precisas, evite saídas de ar ou fontes de calor.
P5: O que devo fazer se o detector de gás disparar o alarme?
Turn off open flames, avoid electrical switches, ventilate immediately, evacuate, and call your gas utility or fire department once outside.
Resumo
Gas leak alarms use small semiconductor sensors—essentially chemical-reactive chips—to turn invisible danger into early warning.
Linked through WiFi and smart valves, they form a modern home safety system that protects you long before you can smell trouble.