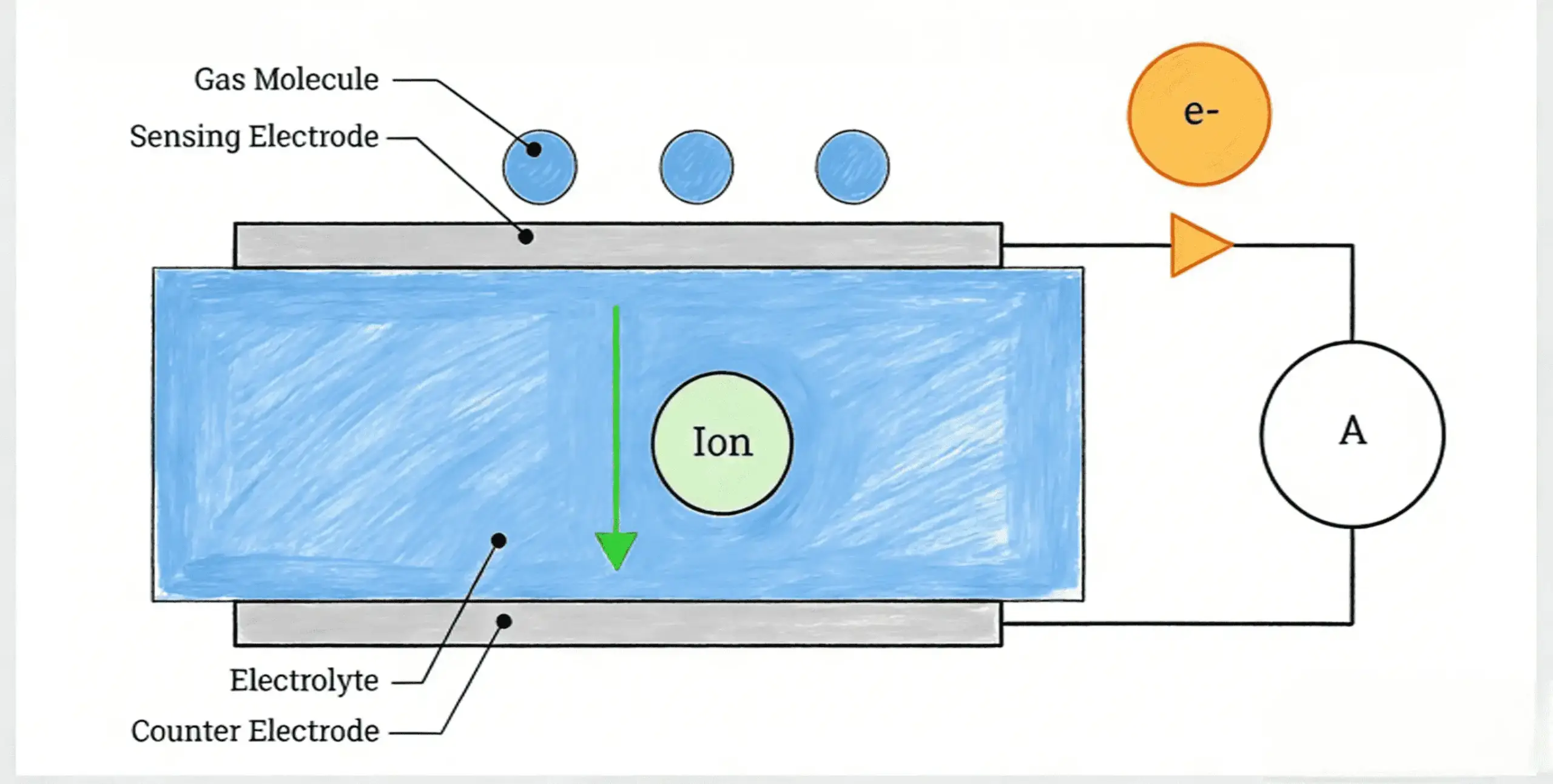
Gas detectors are designed to help identify hazardous gas leaks early, often before a smell is noticeable. In most homes, these devices operate reliably year-round. However, users sometimes notice that gas detectors behave differently in cold environments — such as restarting, entering repeated warm-up cycles, or appearing less stable than expected.
This article explainswhy temperature and power conditions can influence gas detector performance, from a technical and industry-wide perspective. These behaviors are typically related to environmental factors rather than device defects, and understanding them helps ensure proper installation and reliable operation.
How electronic gas detectors work (in simple terms)
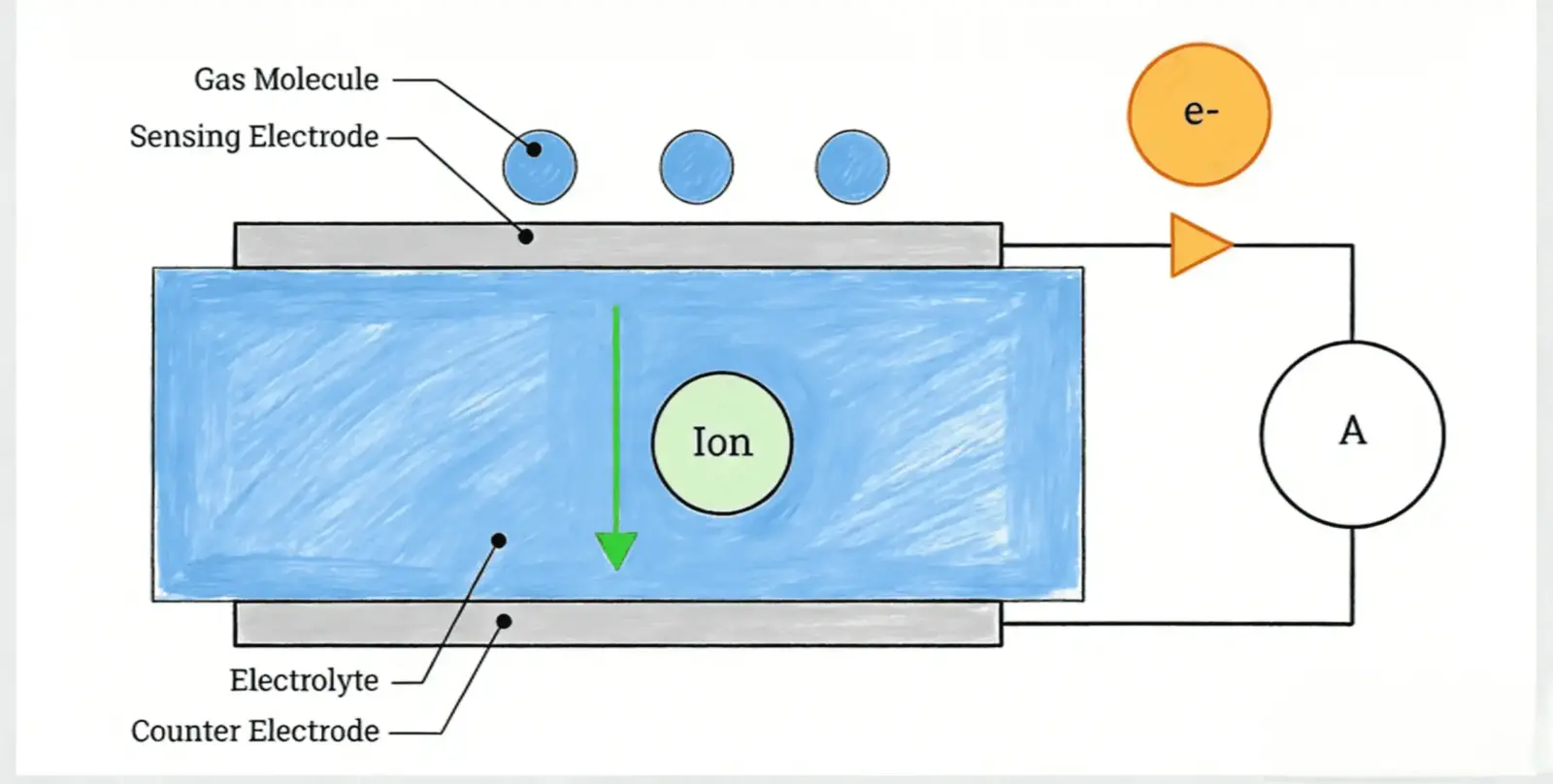
Most modern residential gas detectors useelectronic gas sensorscombined with a control circuit and a power supply. While specific designs vary, the basic working principles are similar across brands:
- A gas sensor reacts chemically or electrically when exposed to target gases
- The sensor operates within a defined temperature range
- A control circuit interprets sensor signals and triggers alerts
- Stable electrical power is required to maintain consistent operation
Unlike purely mechanical devices, electronic gas detectors rely onstable temperature and voltage conditionsto establish a reliable baseline for detection.
Why cold temperatures can affect gas detector behavior
Cold environments introduce challenges for many electronic devices, including gas detectors. Two factors are especially important:power supply stabilityandsensor warm-up requirements.
Power supply stability in low temperatures
Most residential gas detectors use an external AC/DC power adapter or internal power regulation circuitry. In cold environments, especially near or below freezing:
- Power adapters may produceunstable output voltage
- Initial startup current may be insufficient
- Voltage fluctuations can trigger protective resets in the control circuit
When this happens, a gas detector may restart or reset periodically. This behavior is apower stability response, not a sign that the sensor itself is malfunctioning.
Cold temperatures are a known factor affecting power electronics, particularly in unheated spaces such as garages, utility rooms, or storage areas.
Sensor warm-up cycles and cold starts
Gas sensors do not provide accurate readings immediately after power is applied. Most require awarm-up periodto reach a stable operating condition.
In colder environments:
- Warm-up time may increase
- Sensors may repeatedly reinitialize if temperature drops too low
- Devices may display or indicate a “preheating” or initialization state more frequently
This is expected behavior for many electronic gas sensors and reflectsenvironmental conditions, not device failure.
What “rated temperature” really means
Gas detectors are typically specified with a rated operating temperature range, such as “down to -10°C.” This specification is often misunderstood.
Laboratory ratings vs real-world installations
Rated temperature values usually indicate:
- The range in which electronic components and sensorscan function
- Conditions tested undercontrolled laboratory environments
- Stable power supply and limited environmental variation
Real-world installations may differ significantly due to:
- Airflow and drafts
- Power adapter exposure to cold surfaces
- Rapid temperature fluctuations
- Condensation or humidity changes
As a result, performance near the edge of the rated temperature range may vary depending on installation conditions.
Home gas detectors vs industrial-grade systems
Residential gas detectors are designed forhome environments, balancing safety, affordability, and ease of installation.
Industrial gas detection systems typically include:
- Wider operating temperature margins
- Redundant or heated power systems
- Higher sensor power consumption
- Controlled enclosures and professional installation
The differences are not about quality, butintended application. Home gas detectors are optimized for typical indoor residential conditions rather than extreme or unheated environments.
Best practices to reduce cold-weather issues
Most cold-related performance issues can be avoided with proper installation and setup.
Choose an appropriate installation location
Avoid placing gas detectors in areas that experience prolonged low temperatures, such as:
- Unheated garages
- Exterior utility rooms
- Enclosures exposed to outdoor air
Instead, install detectors intemperature-stable indoor areasnear gas appliances or living spaces, following manufacturer placement guidelines.
Pay attention to power supply conditions
- Use the recommended power adapter
- Avoid long or low-quality extension cords
- Ensure the power adapter is not exposed to cold surfaces or drafts
Stable power is essential for consistent detector operation.
Conclusão principal
Variations in gas detector behavior in cold environments are typically caused bytemperature and power-related factors, not sensor defects. Cold conditions can affect power stability and sensor warm-up cycles, especially near the lower edge of rated operating temperatures.
Understanding how environmental conditions influence electronic gas detectors helps ensure proper installation, realistic performance expectations, and reliable safety monitoring throughout the year.
Do gas detectors work in cold temperatures?
Most residential gas detectors are designed to operate within a specified temperature range. In cold environments, especially near the lower limit of that range, performance may vary due to power supply stability and sensor warm-up requirements. This does not usually indicate a sensor failure.
Why does a gas detector reset or restart in cold weather?
Cold temperatures can affect power adapters and electronic components, causing temporary voltage instability. When this happens, a gas detector may restart as a protective response. This behavior is related to environmental conditions rather than a defect in the detector itself.
What does “preheating” mean on a gas detector?
Preheating refers to the sensor warm-up period required for accurate gas detection. In colder environments, this warm-up process may take longer or repeat more frequently until the sensor reaches a stable operating temperature.
Is the rated operating temperature always accurate in real homes?
Rated operating temperatures are determined under controlled laboratory conditions. In real-world installations, factors such as airflow, power supply exposure, and rapid temperature changes can influence performance near the edge of the rated range.
Where should a gas detector be installed in cold climates?
Gas detectors should be installed in temperature-stable indoor areas near gas appliances or living spaces. Unheated garages, exterior utility rooms, or areas exposed to outdoor air may affect performance in cold weather.
Are cold-related issues signs of a faulty gas detector?
In most cases, cold-related behavior such as resets or extended warm-up cycles is caused by environmental and power conditions, not sensor defects. Proper installation and stable power supply usually resolve these issues.