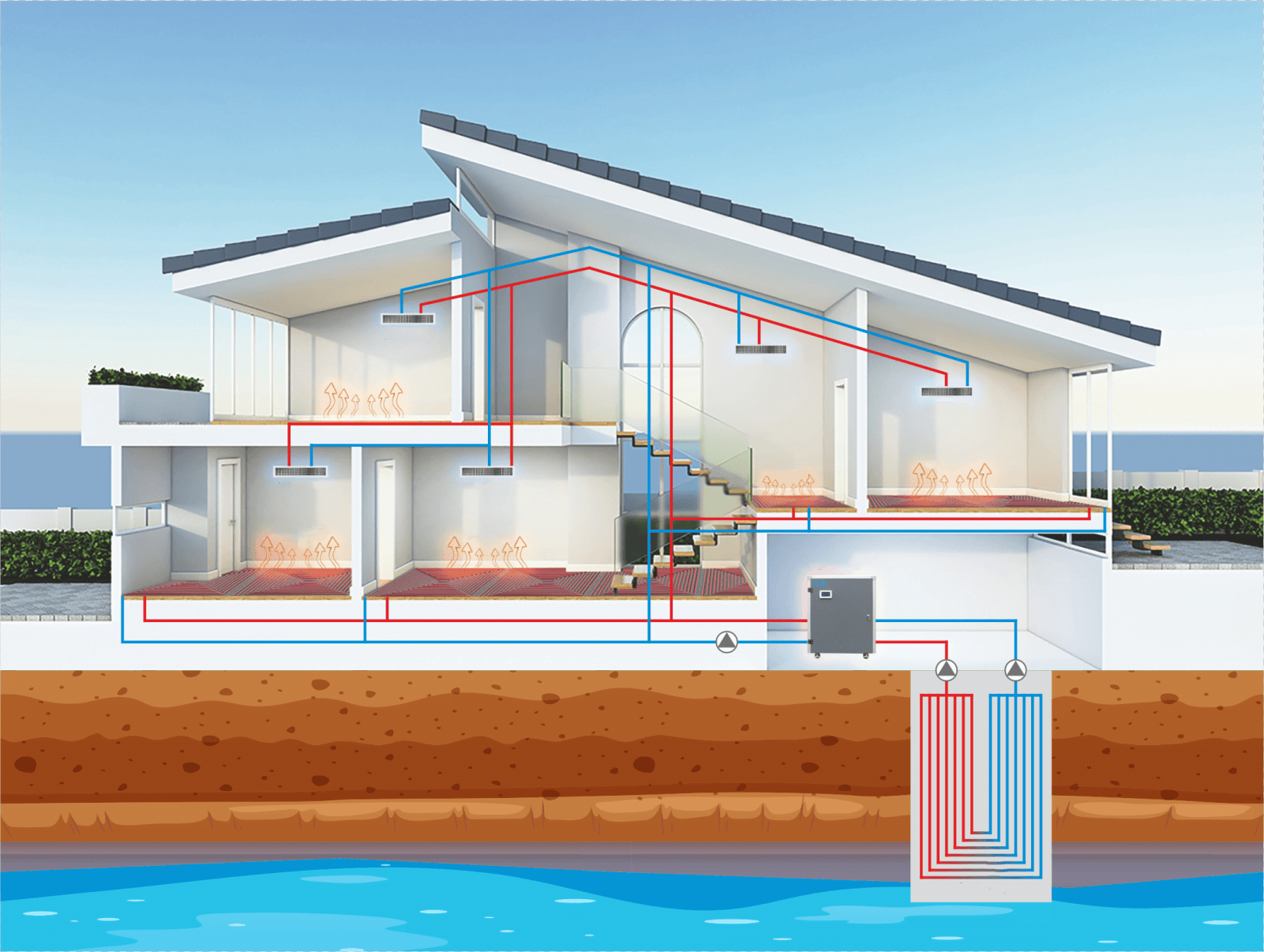
In today’s home environment, proper temperature control is not only related to the comfort of living but also directly affects energy consumption and economic benefits. From underfloor heating to central air conditioning, different types of thermostats play a core role, helping us maintain a constant and comfortable indoor temperature through the changing seasons. With the development of technology, various types of thermostats have appeared on the market, each with its unique functions and applicable scenarios. This article will introduce seven common types of home thermostats through detailed tables and analysis, helping you understand the characteristics and applications of each type of thermostat to make more appropriate choices.
Descripción general del termostato doméstico
To more visually present the basic information and main functions of different thermostats, we first compare these seven common types of home thermostats through a table.
Tabla 1: Comparación de 7 tipos de termostatos y funciones
| Tipo de termostato | Características principales | Entorno recomendado |
|---|---|---|
| Termostato de calefacción por suelo radiante | Controla los sistemas de calefacción por suelo radiante, proporcionando calidez uniforme en el interior. | Residencial, oficina, especialmente en regiones frías. |
| Termostato de bomba de calor | Controla la calefacción y la refrigeración de las bombas de calor, uso eficiente de la energía. | Zonas con cambios estacionales significativos. |
| Termostato de calefacción eléctrica | Gestiona la temperatura de calentadores eléctricos o suelo radiante eléctrico. | Cualquier espacio pequeño que necesite una calefacción rápida. |
| Termostato de aire acondicionado central | Regula el sistema de calefacción y refrigeración de todo un edificio. | Grandes edificios residenciales o comerciales. |
| Termostato del calentador de agua | Controla el equipo de calentamiento de agua para garantizar una temperatura constante del agua. | Casas, hoteles u otros lugares que necesitan mucha agua caliente. |
| Termostato para calentador de agua solar | Gestiona sistemas de agua caliente solar, optimizando la absorción de energía y la eficiencia de conversión. | Áreas con conciencia ambiental y abundante luz solar. |
| Termostato de aire fresco | Controla los sistemas de aire fresco, ajustando la temperatura y la calidad del aire que ingresa al interior. | Zonas residenciales de alta densidad, entornos que necesitan un suministro continuo de aire fresco. |
Through this table, we can preliminarily understand the main functions and applicable environments of each thermostat. Next, we will detail the specific characteristics and applications of each type of thermostat.
Introducción detallada de 7 tipos de termostatos
1. Termostato de calefacción por suelo radiante

Introducción y función:
The underfloor heating thermostat is designed to control floor heating systems. It monitors indoor temperatures through temperature sensors and adjusts the output of underfloor heating to ensure the floor temperature is even and meets the set comfort level. The heat provided by the underfloor system radiates evenly from the ground up, increasing thermal efficiency and reducing air dust movement, which is a significant advantage for people sensitive to respiratory systems.
Uso típico:
In residential and commercial properties, underfloor heating thermostats are commonly used in main living areas such as living rooms, bedrooms, and bathrooms, providing continuous and comfortable heat. Users can set daily or weekly heating schedules based on their living habits to maximize energy efficiency.
The following sections will continue to detail the remaining six common types of home thermostats, their functions, typical usage, and characteristics.
2. Termostato de bomba de calor

Introducción y función:
The heat pump thermostat controls heat pump systems, which can provide both heating and cooling functions, making it very suitable for areas with significant temperature changes throughout the year. The heat pump thermostat can optimize the operation of the heat pump, improving energy efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Uso típico:
Heat pump thermostats are typically installed in residential or commercial buildings that require year-round temperature regulation. Users can set temperature thresholds to ensure indoor temperatures remain comfortable regardless of external temperature changes.
3. Termostato de calefacción eléctrica

Introducción y función:
The electric heating thermostat controls electric heating equipment, such as electric radiators or electric heated floors. This type of thermostat can precisely regulate the output of electric heating devices to maintain a stable indoor temperature.
Uso típico:
In homes or offices, electric heating thermostats are suitable for quickly heating small spaces. Users can adjust the temperature as needed or set timers to automatically turn heating on or off at specific times.
4. Termostato del aire acondicionado central

Introducción y función:
The central air conditioning thermostat manages the central air conditioning system, controlling the heating and cooling of an entire building or house. This thermostat can achieve complex multi-zone temperature control, improving overall energy efficiency.
Uso típico:
Central air conditioning thermostats are usually installed in large residential or commercial buildings, setting different temperatures for different areas or floors to achieve precise temperature control.
5. Termostato del calentador de agua

Introducción y función:
The water heater thermostat controls the operation of water heaters to ensure constant water temperature and avoid energy waste. This thermostat can precisely adjust the temperature of the water heater, suitable for homes, hotels, or other places that require a large amount of hot water.
Uso típico:
Users can set the water temperature according to personal preferences and needs. Water heater thermostats can also set specific heating schedules to save energy and provide hot water when needed.
6. Termostato para calentador de agua solar

Introducción y función:
The solar water heater thermostat manages the temperature exchange between solar collectors and storage tanks. It optimizes the absorption and conversion of energy, ensuring system efficiency is maximized while preventing overheating.
Uso típico:
In sun-rich areas, solar water heater thermostats can automatically adjust hot water production based on solar radiation intensity, ensuring a continuous supply of efficient and environmentally friendly hot water.
7. Termostato de aire fresco

Introducción y función:
The fresh air thermostat controls the operation of fresh air systems, which are responsible for introducing processed fresh air indoors. It can adjust the temperature of the incoming air, improving air quality and providing a healthy, comfortable environment for living spaces.
Uso típico:
Fresh air thermostats are particularly important in high-density residential areas or industrial environments. They can automatically adjust the intake based on the temperature difference between the outside and inside, ensuring indoor air is fresh and at a suitable temperature.
This detailed introduction provides specific information and usage guidelines for various thermostats, helping users choose the most suitable thermostat based on their actual needs and living environments. The following sections will involve more discussions on international specifications and standards, ensuring global users can safely and effectively use these devices.
Métodos de cableado y estrategias de control
Next, we will detail the wiring methods and control strategies of various thermostats through another table, ensuring you can choose the most suitable configuration based on your home’s specific needs.
Tabla 2: 7 tipos de termostatos, métodos de cableado y estrategias de control
In this section, we will detail the wiring methods and control strategies of various thermostats through a table, which is crucial for ensuring correct installation and optimal performance of the devices.
| Tipo de termostato | Método de cableado | Estrategia de control |
|---|---|---|
| Termostato de calefacción por suelo radiante | Usually includes power, ground, and control wires, connected to the underfloor heating system’s power and control ends. | Control diferencial de temperatura, control PID, funciones de aprendizaje programables e inteligentes. |
| Termostato de bomba de calor | Needs to be connected to the heat pump’s power and control ends, may require a multi-wire system to support heating and cooling functions. | Control diferencial de temperatura, control de horario, ajuste inteligente. |
| Termostato de calefacción eléctrica | Sistemas simples de dos o tres cables, que controlan directamente elementos calefactores eléctricos. | Control diferencial de temperatura, control de temporizador, algunos modelos admiten control remoto. |
| Termostato de aire acondicionado central | Sistemas complejos de múltiples cables, que requieren conexión a varias partes del sistema de aire central. | Control de zona, control conjunto de temperatura y humedad, control inteligente y remoto. |
| Termostato del calentador de agua | Cableado de al menos dos cables, que controle el interruptor de encendido del calentador. | Control diferencial de temperatura, control de optimización de eficiencia. |
| Termostato para calentador de agua solar | Includes temperature sensor wires, power wires, and control wires, to optimize solar energy collection and use. | Control de prioridad de temperatura, monitoreo de eficiencia, ajuste automático. |
| Termostato de aire fresco | Generalmente es necesario conectarse con sensores de temperatura interiores y exteriores y con una unidad de aire fresco. | Automatic adjustment based on indoor and outdoor temperature difference, timer control, air quality feedback control. |
Through this table, we can see the differences in wiring methods and control strategies among different types of thermostats, which directly affect the installation process and daily operation efficiency of the devices.
Especificaciones y normas internacionales
For thermostats used across countries and sold in international markets, understanding and complying with the electrical specifications and safety standards of different countries and regions is extremely important. Here is a table summarizing some of the main market specifications and wiring standards.
Tabla 3: Especificaciones y estándares de cableado en diferentes países y regiones
| País/Región | Requisitos de voltaje y frecuencia | Regulaciones y Certificaciones | Requisitos especiales de cableado |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 120 V/60 Hz | Certificación UL, Código Eléctrico NEC | Requisitos estrictos para las medidas de puesta a tierra y protección |
| EU | 220-240 V/50 Hz | Marcado CE, conformidad con RoHS | Must comply with the EU’s Low Voltage Directive and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive |
| Porcelana | 220 V/50 Hz | Certificación CCC | Debe adaptarse a la alta densidad de población y a los requisitos de alta frecuencia de uso. |
| Japón | 100 V/50 Hz o 60 Hz | Certificación PSE | Normas específicas antisísmicas y resistentes al fuego |
| Australia | 230 V/50 Hz | Certificación SAA | La instalación debe considerar los efectos del clima exterior, como la impermeabilización y la protección UV. |
This table shows some of the key electrical and safety standards to consider when operating in the global market, helping manufacturers and users ensure product compatibility and safety.
Modos de control inteligente: Innovación en termostatos modernos
As technology continues to advance, the widespread adoption of smart home systems has greatly changed our way of managing home appliances, and thermostats are no exception. Smart control modes make thermostats not just simple temperature adjustment devices but a system that can increase energy efficiency, enhance comfort, and simplify daily life. This section will explore the control methods of smart thermostats and their benefits.
Características básicas de los termostatos inteligentes
The main difference between smart thermostats and traditional thermostats is their connectivity and automation features. These thermostats are usually connected to the home network through Wi-Fi or other wireless technologies (such as Zigbee or Z-Wave), allowing users to remotely control the home temperature via smartphone apps, tablets, or voice assistants (like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit).
Funciones principales del control inteligente
- Mando a distancia: Users can view and adjust the home temperature settings from anywhere via an app, whether at the office or on vacation.
- Programación automática: Smart thermostats can automatically set temperature schedules based on users’ daily activity patterns. For example, it can start heating the home automatically before you usually get up, ensuring the room is warm and comfortable when you wake up.
- Análisis de eficiencia energética: Many smart thermostats provide detailed energy consumption reports and analyses, helping users understand how their heating and cooling habits affect energy consumption and how to adjust settings to reduce energy costs.
- Geocercado: Using the location of users’ smartphones, smart thermostats can know when users leave home or are on their way home. The system adjusts the temperature accordingly to optimize energy efficiency and provide a comfortable environment when users arrive.
- Control por voz: Once integrated with smart home assistants, users can simply use voice commands to adjust temperature settings, greatly increasing convenience and accessibility.
- Preferencias de aprendizaje: Some high-end smart thermostats, like the Nest Learning Thermostat, have the ability to learn users’ preferences and can automatically establish a suitable temperature schedule for the home within a few days without much user intervention.



Aplicaciones prácticas de los termostatos inteligentes
Considering the potential of smart thermostats to improve energy efficiency and user comfort, many modern homes and offices have begun deploying these devices. For example, a family might use a smart underfloor heating thermostat to preheat rooms in winter, while optimizing cooling efficiency with a central air conditioning thermostat in summer.
The integration and application of smart thermostats not only enhance the comfort of living and working environments but also help achieve a more sustainable lifestyle by precisely controlling and intelligently adjusting to reduce energy waste. As technology continues to advance and user awareness increases, it is expected that smart thermostats will become an important component of home automation in the future.
Efectos de ahorro energético y datos indicativos de los termostatos inteligentes
Smart thermostats not only improve the comfort and convenience of homes, but they also play a crucial role in energy saving and reducing environmental impact. Through smart features, these devices can optimize the timing of heating and cooling, reducing unnecessary energy consumption, thereby bringing significant energy-saving effects to users. This section will explore the energy-saving effects of smart thermostats and provide some specific energy-saving data.
Funciones de ahorro de energía
- Ajuste automático: Smart thermostats can automatically adjust settings based on outdoor temperatures and indoor activity patterns, avoiding excessive heating or cooling, which directly reduces energy waste.
- Programación eficiente: By learning users’ living habits, smart thermostats can automatically create efficient heating and cooling schedules. For example, they automatically reduce the operation of heating or air conditioning during times when users are typically not at home.
- Optimización de detalles: Smart thermostats can also achieve energy savings by making small adjustments to temperature settings (such as lowering by 1-2°F/about 0.5-1°C), and these small changes usually do not affect the comfort of the occupants.
Datos indicativos de ahorro de energía
The energy-saving effects of smart thermostats can be more clearly demonstrated through the following data:
- Reducción del consumo de energíaSe estima que los termostatos inteligentes pueden reducir el consumo de energía del hogar entre un 10% y un 12%.
- Ahorro anual: On average, homes can save about 10% to 23% on heating costs and 15% on air conditioning costs per year by using smart thermostats.
- Retorno de la inversión a largo plazo: Although the initial investment for smart thermostats is relatively high, according to data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the average family can recoup this cost through energy savings within two years.
These data show that although smart thermostats cost more than traditional thermostats, they can achieve cost-effectiveness in the long run by significantly reducing energy costs. More importantly, this type of thermostat helps households manage and use energy more effectively through automation and intelligence features.
Resumen
Los termostatos inteligentes no solo mejoran la comodidad y conveniencia de nuestras vidas,
but their energy-saving features also help promote homes towards a greener, more sustainable direction. As technology continues to advance, the market for smart thermostats is expected to expand further, and their energy-saving technologies will continue to improve, contributing more to the global improvement in energy efficiency.
Choosing and installing the right thermostat is crucial for enhancing the comfort and energy efficiency of home and office environments. Through the introduction and analysis in this article, we hope readers can better understand the functions, applicable scenarios, wiring methods, and international specification differences of various thermostats, thereby choosing the most suitable thermostat for their needs. In today’s increasingly globalized world, the correct selection and use of these devices not only enhance the energy efficiency of individuals and businesses but also ensure compliance with regulations and standards in different regions, achieving safe, efficient environmental control.